Pandas DataFrame ‘applymap()’ Method.
Table Of Contents:
- Syntax ‘applymap( )’ Method In Pandas.
- Examples ‘applymap( )’ Method.
- Difference Between apply() and applymap() .
(1) Syntax:
DataFrame.applymap(func, na_action=None, **kwargs)Description:
Apply a function to a Dataframe elementwise.
This method applies a function that accepts and returns a scalar to every element of a DataFrame.
Parameters:
- func: callable – Python function, returns a single value from a single value.
- na_action: {None, ‘ignore’}, default None – If ‘ignore’, propagate NaN values, without passing them to func.
- **kwargs – Additional keyword arguments to pass as keywords arguments to func.
Returns:
- DataFrame : Transformed DataFrame.
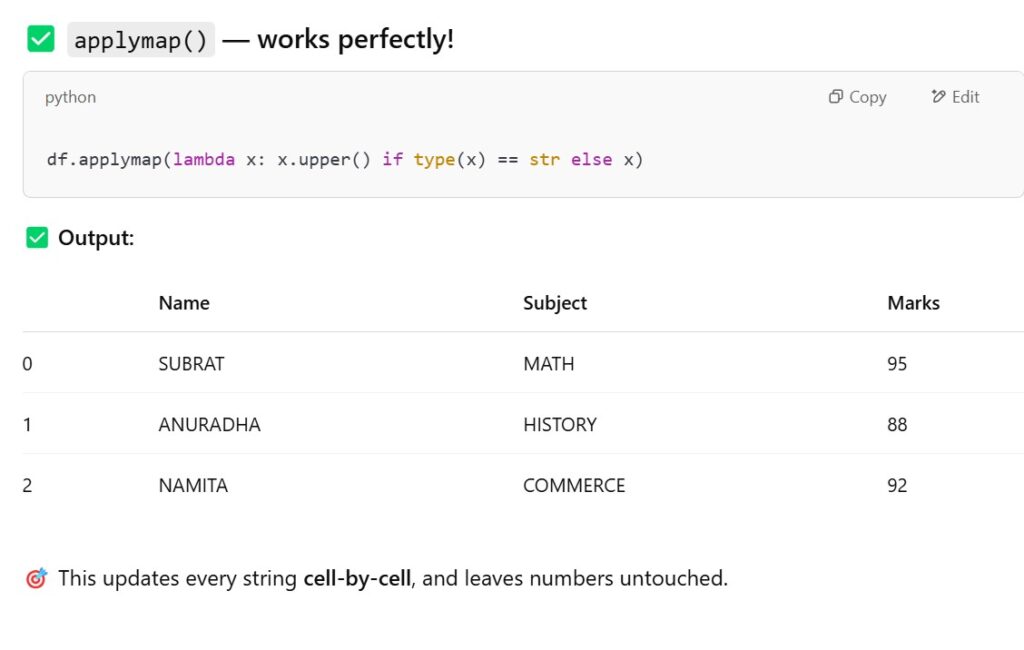
(2) Examples Of applymap() Method:
Example-1
import pandas as pd
student = {'Name':['Subrat','Abhispa','Arpita','Anuradha','Namita'],
'Roll_No':[100,101,102,103,104],
'Subject':['Math','English','Science','History','Commerce'],
'Mark':[95,88,76,73,93],
'Gender':['Male','Female','Female','Female','Female']}
student_object = pd.DataFrame(student)
student_objectOutput:

# Counting Number Of Characters In Each Value.
student_object.applymap(lambda x: len(str(x)))Output:

# Adding With Itself
student_object.applymap(lambda x: x + x)
Output:

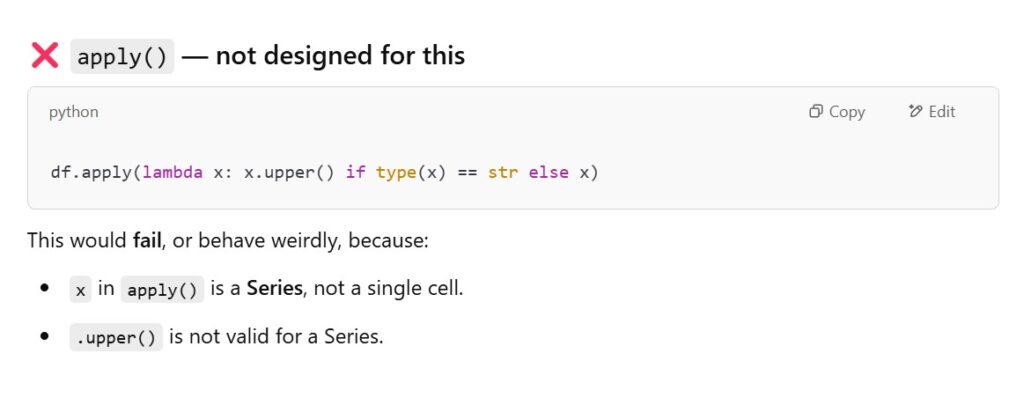
(3) Difference Between apply() and applymap() .
- The apply() method will accept only the Series object as input.
- Hence whatever operation on serries can be performed here.
- The apply() method will not iterate on individual elements of the dataframe.
- The applymap() method will accept the individual elements of the data frame.
- Hence you can perform any individual operation on the each element of the dataset.
- The applymap() method will iterate on individual elements of the data frame.