How To Fetch Code From Remote?
Table Of Contents:
- What Is Git Fetch?
- Examples Of Git Fetch?
- Difference Between Fetching and Pulling?
(1) What Is GIT Fetch?
- You can use
git fetchto know the changes done in the remote repo/branch since your last pull. - This is useful to allow for checking before doing an actual pull, which could change files in your current branch and working copy (and potentially lose your changes, etc).
(2) Examples Of GIT Fetch?
Example-1: Fetching Remote Repository
git fetch <repository Url> git fetch https://github.com/Subrat/Project.git- It will download all the changes and keep them in a separate file.
- It won’t update your working directory.
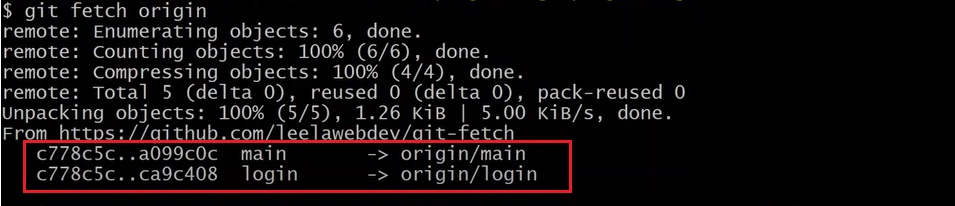
- Here two new branches have been downloaded to local from remote, “origin/main” and “origin/login”
- You can now check the difference between your local and remote branches, to check for new changes.
Example-2: Checking The Difference Between Branches.
git diff <LOCAL BRANCH> <REMOTE BRANCH> git diff main origin/main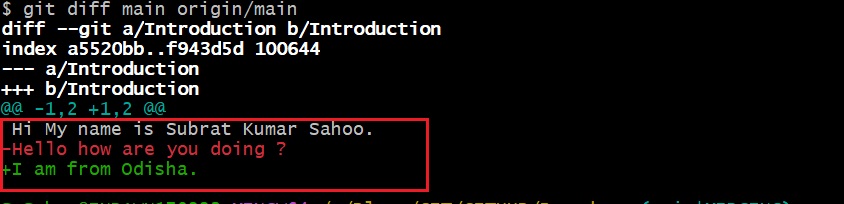
- After you see the difference, if there is any conflict, that means the same file and same line other developer has added the code, you can resolve it manually.
- You can use the “Beyond Compare” tool to resolve the conflict.
Example-2: Fetching A Specific Branch
git fetch <remote URL> <branch name> git fetch https://github.com/Subrat/Project.git branch1- It will only download the ‘branch1’ branch.

- Here you can see that, your local branch is 2 commits behind.
- You can check those commits and merge them to the local branch.
(3) Once I Done “git remote add origin ” Do I Again Need To Specify The Remote Repository URL?
- No, you don’t need to mention the remote URL every time you use
git fetchafter running:
git remote add origin <repository-URL>
- Since
originis now linked as the default remote, you can simply run:
git fetch origin
- You can also fetch a specific branch.
(4) What You Do After Fetching The Remote Branch ?
- Once you fetch the remote repository “origin”, you merge the changes to your local repository.
Step-1: Fetch The Remote Repository
git fetch origin main
Step-2: Merge The Remote Repository To The Local Branch
git merge origin/main- Note: This command will merge the remote changes to the local branch. Here “origin/main” represents the remote location repository branch.
- Question: But the question is on which branch it will merge ?
- Answer: The
git merge origin/maincommand will merge changes into the currently checked-out branch (your active branch). - If you don’t switch branches before merging, Git will merge into whatever branch you’re currently on.
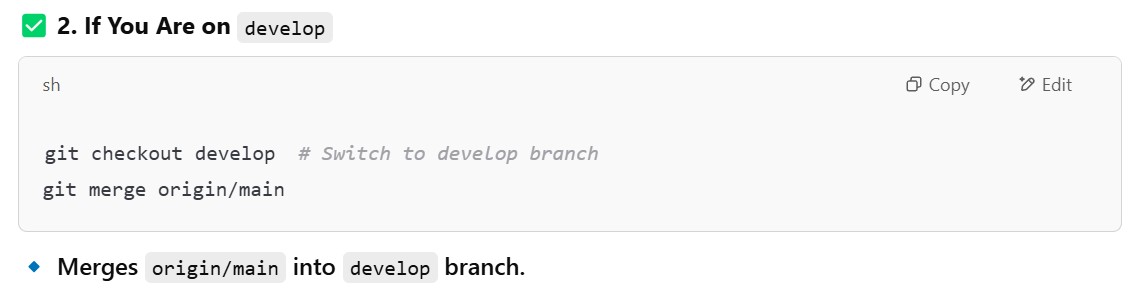
- Hence first checkout the branch you want to merge and then run the merge command.
- Or else it will be merged to the branch you dont want to merge.