GenAI – Semantic Chunking
Table Of Contents:
- What Is Semantic Chunking ?
- When To Use Semantic Chunking ?
- Advantages Of Semantic Chunking.
- Disadvantages Of Semantic Chunking.
- Examples Of Semantic Chunking.
- Techniques Available For Semantic Chunking .
(1) What Is Semantic Chunking ?



(2) When To Use Semantic Chunking ?



(3) How Semantic Chunking Works ?





(4) Tools & Libraries for Semantic Chunking
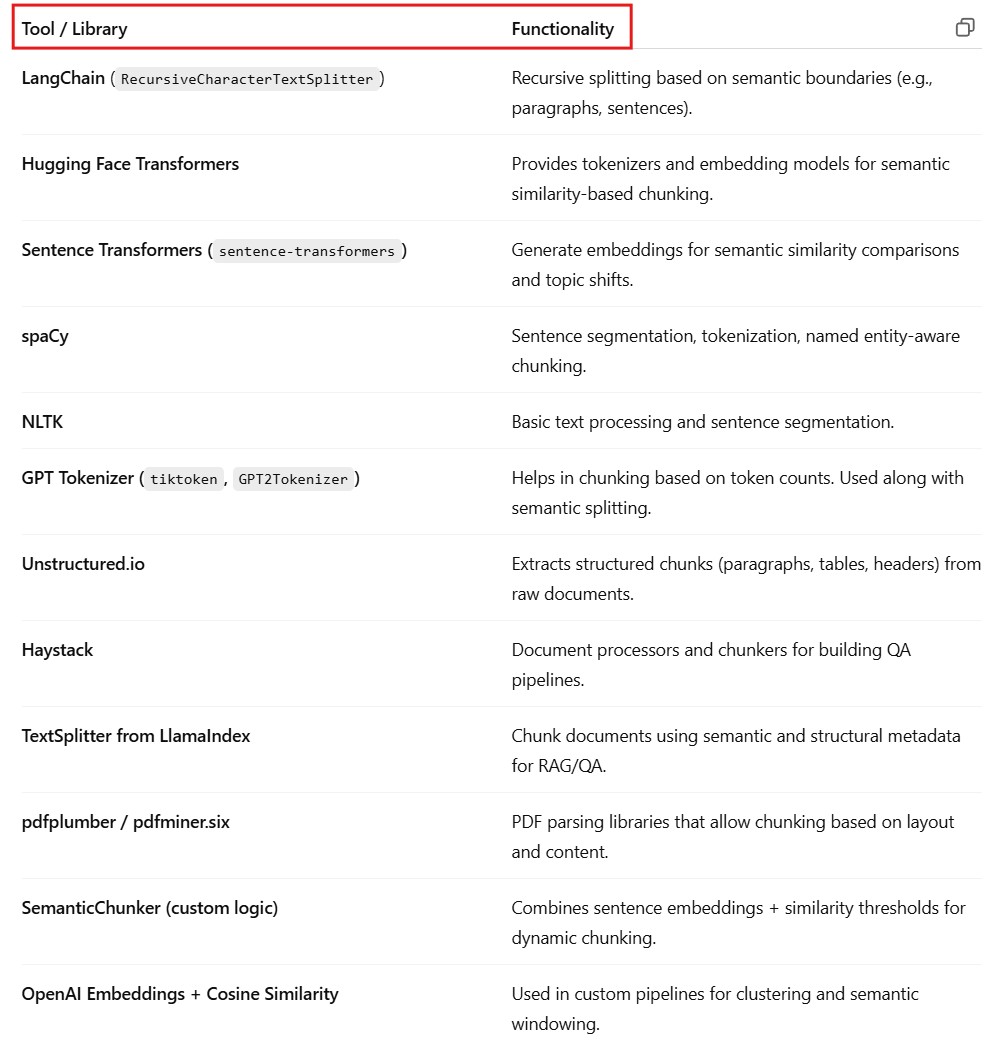
(5) Advantages Of Semantic Chunking.

(6) Disadvantages Of Semantic Chunking.


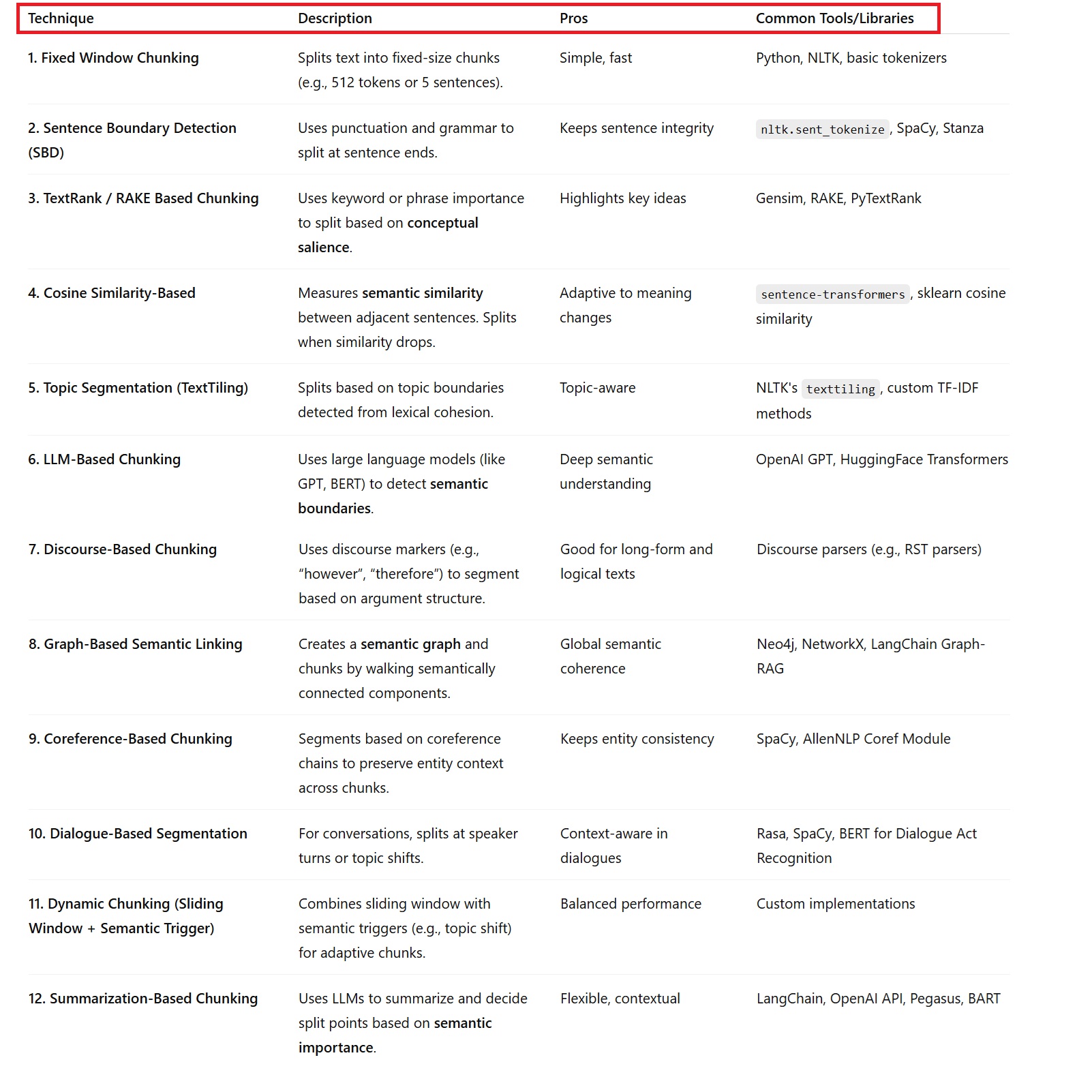
(6)Techniques Available For Semantic Chunking.
(7) Examples Of Semantic Chunking.
Example 1: Using LangChain’s RecursiveCharacterTextSplitter
- This splits the text based on semantic boundaries like paragraphs, sentences, etc.
from langchain.text_splitter import RecursiveCharacterTextSplitter
text = """Large Language Models like GPT need chunking when processing long documents.
Splitting content semantically improves understanding.
For example, splitting at paragraphs makes the context more coherent."""
text_splitter = RecursiveCharacterTextSplitter(
chunk_size=100, # approx token-based size
chunk_overlap=20,
separators=["\n\n", "\n", ".", "!", "?", " ", ""]
)
chunks = text_splitter.split_text(text)
print(chunks)

Example 2: Semantic Similarity-based Chunking Using Sentence Transformers
- This example detects topic shifts using cosine similarity between sentence embeddings.
- If the similarity between the sentence is more than 0.7 then it grouped it together or else it will create a new chunk.

from sentence_transformers import SentenceTransformer
from sklearn.metrics.pairwise import cosine_similarity
text = """Machine learning is used to build intelligent systems.
Supervised learning is a type of machine learning.
Natural language processing is a popular ML domain.
Transformers are widely used in NLP.
Stock markets use time-series forecasting.
Cryptography is used for security."""
sentences = text.split('\n') # simulate paragraph-level chunks
model = SentenceTransformer('all-MiniLM-L6-v2')
embeddings = model.encode(sentences)
# Set similarity threshold to define topic change (0.7 is moderate)
threshold = 0.7
chunks = []
chunk = [sentences[0]]
for i in range(1, len(sentences)):
similarity = cosine_similarity([embeddings[i]], [embeddings[i-1]])[0][0]
if similarity > threshold:
chunk.append(sentences[i])
else:
chunks.append(" ".join(chunk))
chunk = [sentences[i]]
chunks.append(" ".join(chunk))
print(chunks)

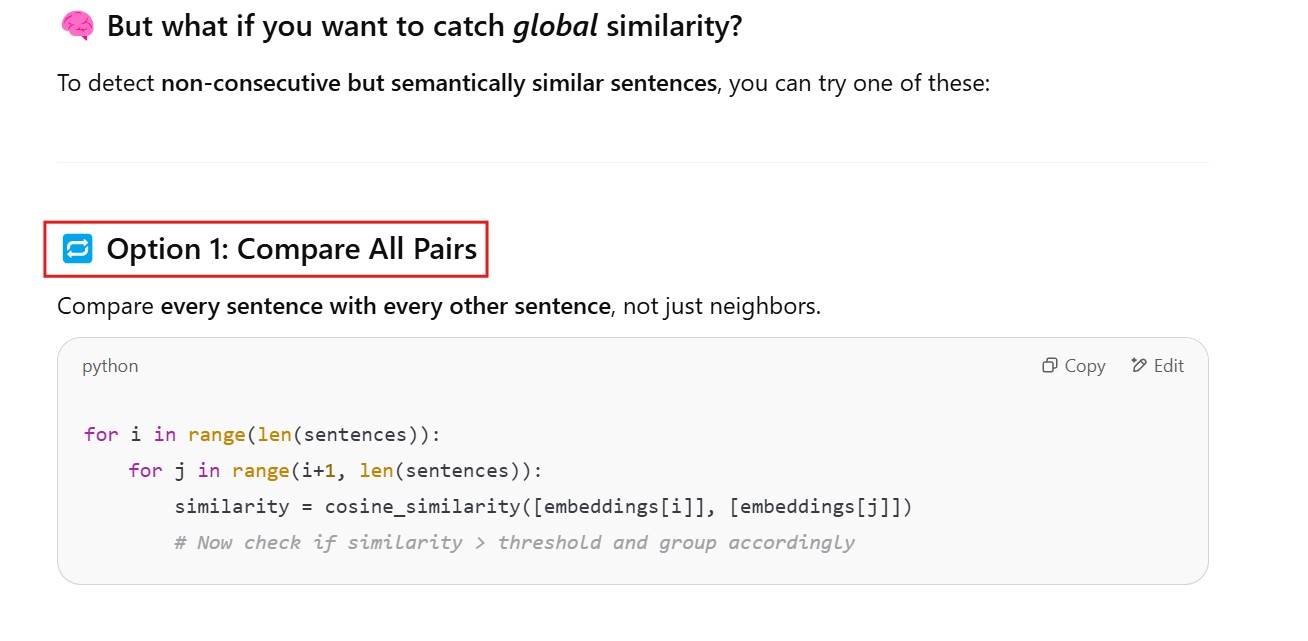
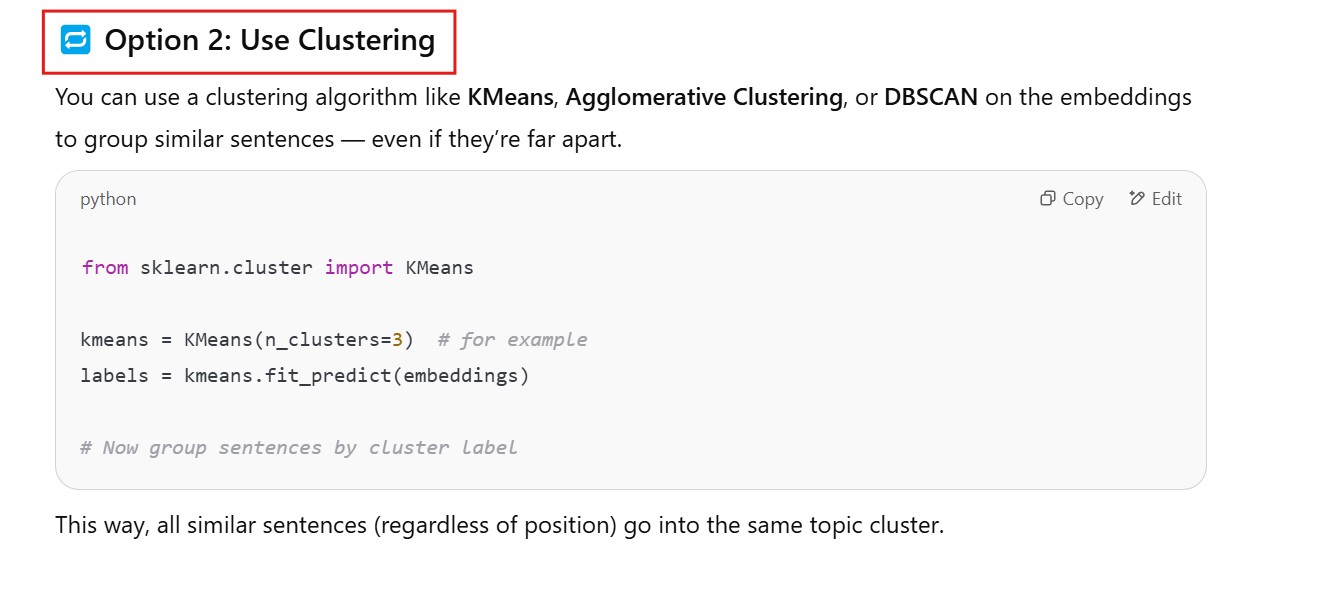
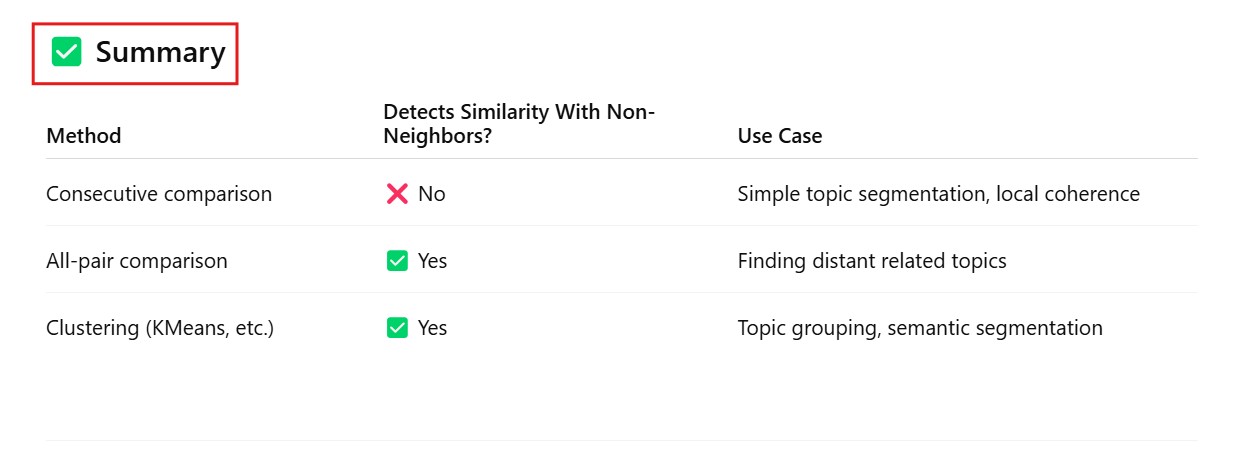
Example 3: Using spaCy for Sentence-based Chunking
- spaCy can be used to split a document into sentences semantically.
import spacy
nlp = spacy.load("en_core_web_sm")
text = """GPT-4 is a powerful language model. It is used in chatbots, summarization, and translation.
Traditional models required more training data. Now, few-shot learning is sufficient."""
doc = nlp(text)
sentences = [sent.text for sent in doc.sents]
print(sentences)
Example 4: Using Unstructured.io for Document-aware Semantic Chunking
- spaCy can be used to split a document into sentences semantically.
from unstructured.partition.pdf import partition_pdf
elements = partition_pdf(filename="sample.pdf")
# Extract semantic chunks (e.g., paragraphs, tables)
for element in elements:
print(element.text)

