-
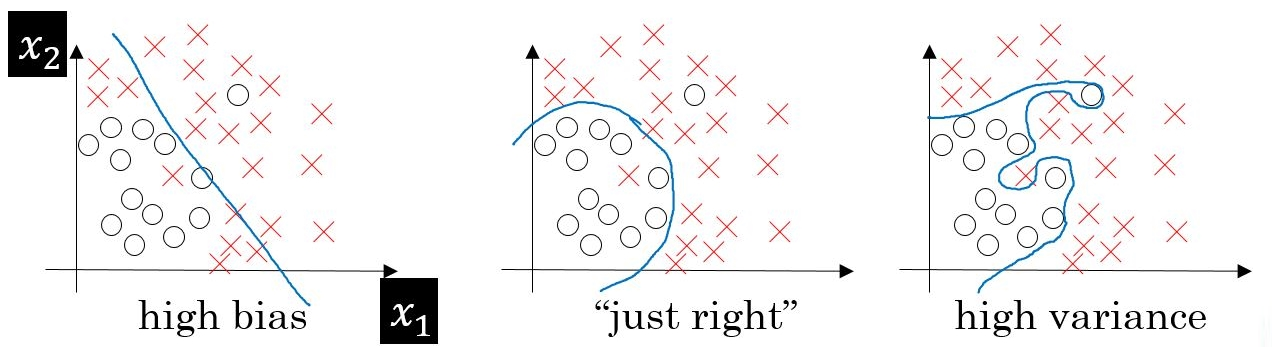
Bias Vs Variance !!
Bias Vs Variance Table Of Contents: Introduction. Errors In Machine Learning. What Is Bias? Why Does Bias Occurs In Model? Effect Of Bias In Our Model. Way To Reduce High Bias. What Is Variance? Why Does Variance Occurs In Model? Effect Of Variance In Our Model. Way To Reduce High Variance. What Is Bias Variance Trade-Off? (1) Introduction. Bias and variance are two important concepts in machine learning that help in understanding the behaviour and performance of a model. They represent different sources of error in a machine learning algorithm and can provide insights into how well the model is
-

Regularization In Machine Learning.
Regularization In Machine Learning Table Of Contents: What Is Regularization? Types Of Regularization Techniques. L1 Regularization (Lasso Regularization). L2 Regularization (Ridge Regularization). Elastic Net Regularization. Why It Is Called Penalty? What Does The Penalty Do Comparison Of L1 and L2 Penalty How to Choose the Regularization Type? Effect of Regularization Parameter (𝜆) Can We Apply Regularization To All The Machine Learning Models ? (1) What Is Regularization? We need a regulator for our model to have control of the learning, we can have control to avoid overfitting of the model. Regularization in machine learning is a technique used to prevent
-
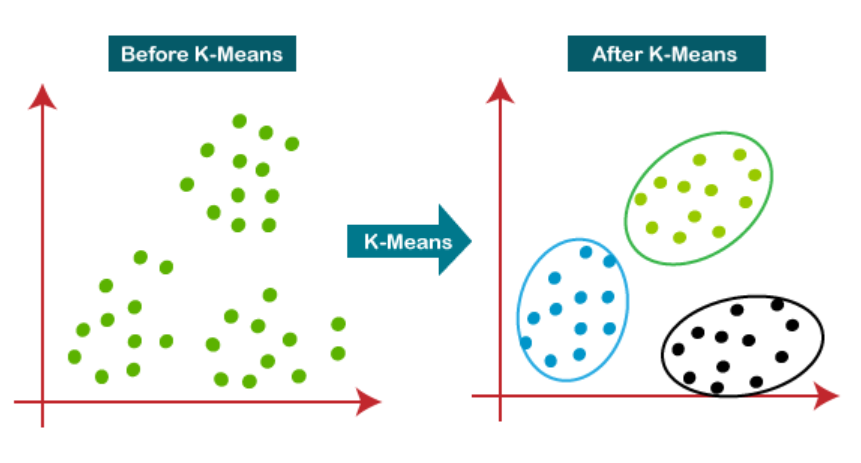
K – Means Clustering Algorithm.
K – Means Clustering Table Of Contents: What Is Clustering? What Is The K-Means Algorithm? How Does The K-Means Algorithm Work? How to Choose the Right Number of Clusters in K-Means Clustering? Advantages & Disadvantages Of K-Means Clustering. Applications Of K-Means Clustering. (1) What Is Clustering ? Clustering is a technique used in machine learning and data analysis to group similar objects or data points together based on their inherent characteristics or patterns. It is an unsupervised learning method, meaning that it does not rely on labelled data or predefined categories. The goal of clustering is to identify natural groupings
-
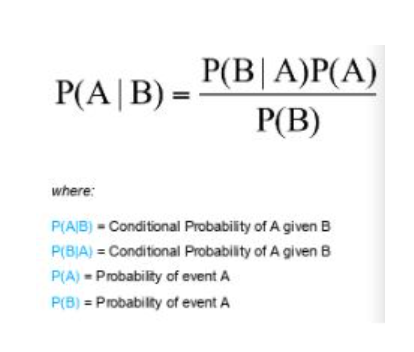
Naive Bayes Algorithm Paper Work
Naive Bayes Algorithm Table Of Contents: What Is Bayes Theorem? What Is Naive Bayes Algorithm? Example How Naive Bayes Solves Classification Problem. (1) What Is Bayes Theorem? (2) What Is Naive Bayes Algorithm? (3)Example: We need to calculate the probability of Spam and Not Spam. We will label the new data points based on the maximum probability between two probability. Here X1 and X2 are independent events hence probabilities are multiplied together. What Is Total Probability? (2) Assumption Made By Naive Bayes The Naive Bayes algorithm assumes that all features are independent of each other if you already know the
-
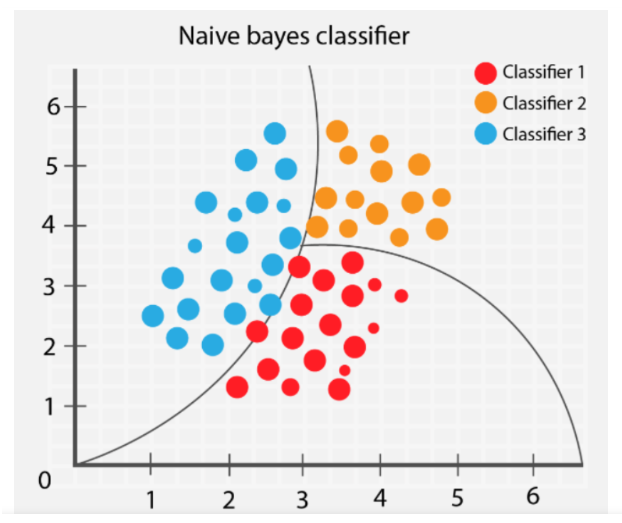
Naive Bayes Algorithm
Naive Bayes Algorithm Table Of Contents: What Is Naive Bayes Algorithm? What Is Conditional Probability? What Is Bayes Theorem? Why Is It Called Naive Bayes? Assumptions Of Naive Bayes Algorithm. What Is Bayesian Probability? How Does The Naive Bayes Algorithm Works? Types Of Naive Bayes Model. Pros & Cons Of Naive Bayes Algorithm. Applications Of Naive Bayes Algorithm. (1) What Is Naive Bayes Algorithm? The Naive Bayes algorithm is a probabilistic machine learning algorithm commonly used for classification tasks. It is based on Bayes’ theorem, which describes the probability of an event given prior knowledge or evidence. The “naive” assumption
-
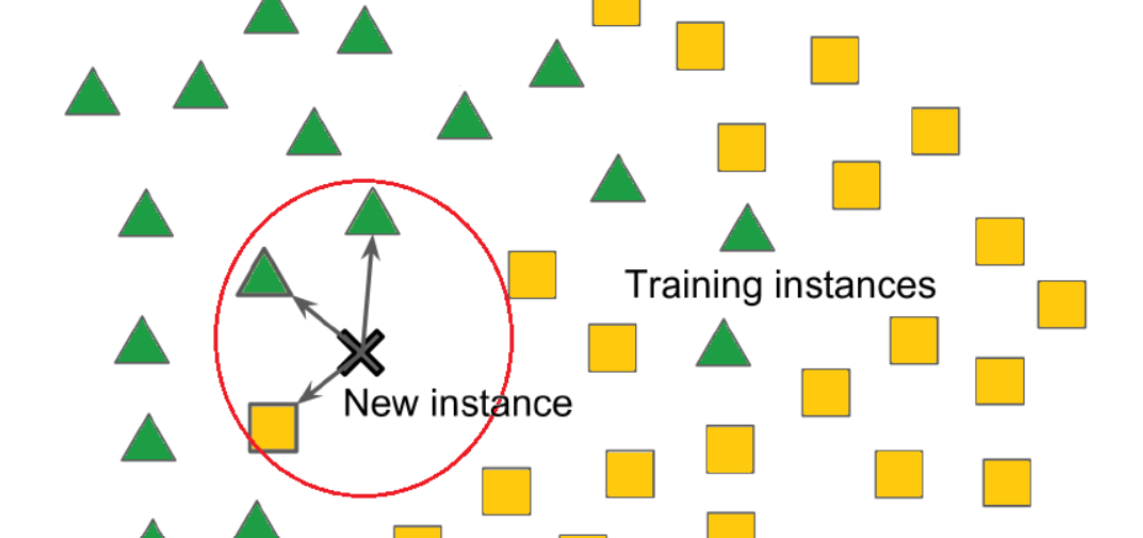
K – Nearest Neighbors Algorithm
K – Nearest Neighbors Table Of Contents: What Is K – Nearest Neighbor Algorithm? How Does The KNN Algorithm Work? How Do We Choose The Factore K? Distance Metrics Used In KNN Algorithm. Advantages & Disadvantages Of KNN Algorithm. Applications Of KNN Algorithm. (1) What Is K – Nearest Neighbor? The k-nearest neighbours (k-NN) algorithm is a popular supervised machine learning algorithm used for both classification and regression tasks. It operates based on the principle that data points with similar features tend to belong to the same class or have similar output values. It is widely disposable in real-life scenarios
-

Support Vector Machine
Support Vector Machine Table Of Contents: What Is a Support Vector Machine? How Does Support Vector Machine Work? Types Of Support Vector Machine Algorithms. Mathematical Intuition Behind Support Vector Machine. Margin In Support Vector Machine. Optimization Function and Its Constraints. Soft Margin SVM. Kernels In Support Vector Machine. How To Choose A Right Kernel? (1) What Is Support Vector Machine? The Support Vector Machine (SVM) algorithm is a supervised machine learning algorithm used for classification and regression tasks. It is particularly effective in solving binary classification problems but can also be extended to multi-class classification. SVMs can be used for
-

Weak Learner vs. Strong Learner.
Weak Learner Vs. Strong Learner Table Of Contents: Introduction. Weak Learner. Strong Learner. Conclusion. (1) Introduction: In machine learning, the terms “strong learner” and “weak learner” refer to the performance and complexity of predictive models within an ensemble or learning algorithm. These terms are often used in the context of boosting algorithms. (2) Weak Learner: A weak learner is a model that performs slightly better than random guessing or has limited predictive power on its own. Weak learners are typically simple and have low complexity, such as decision stumps (a decision tree with only one split), shallow decision trees, or
-
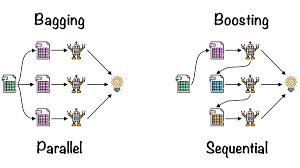
Bagging, Boosting & Stacking Technique.
Bagging, Boosting & Stacking Technique Introduction: Bagging and boosting are two ensemble learning techniques commonly used in machine learning. Both approaches aim to improve the predictive performance of individual models by combining multiple models together. However, they differ in how they construct and combine the models. (1) Bagging Technique:(Bootstrap Aggregating): Bagging involves creating multiple copies of the original training dataset through a technique called bootstrapping. Bootstrapping randomly samples the training data with replacement, resulting in different subsets of data for each model. Each model in the ensemble is trained independently on one of the bootstrapped datasets. Bagging typically uses majority
-
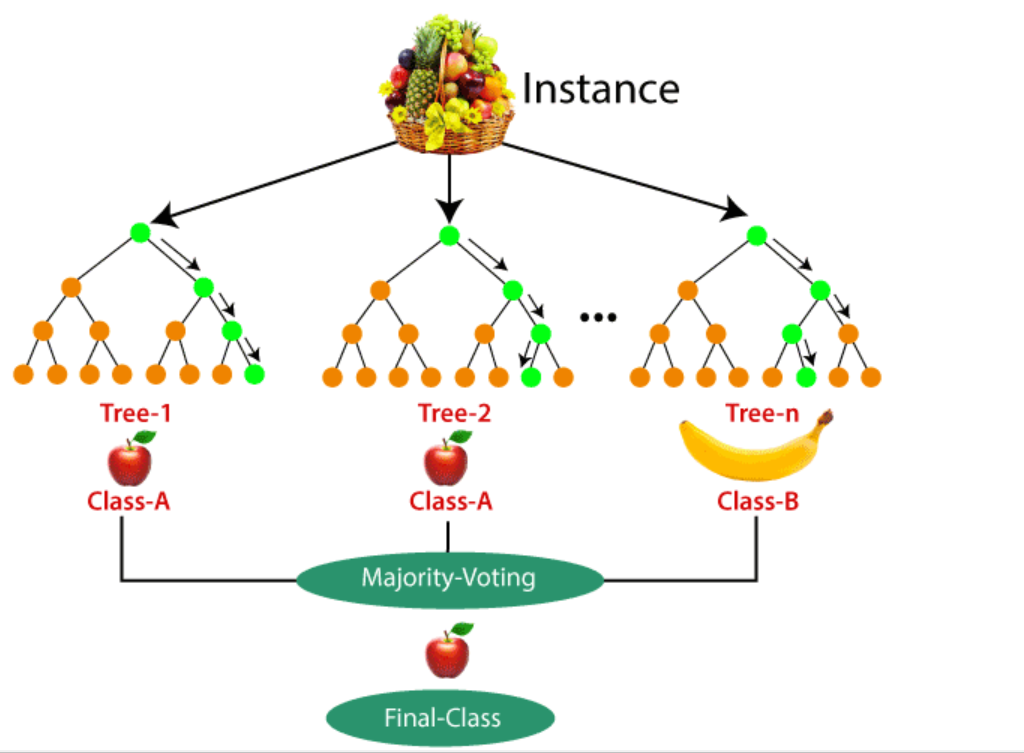
Random Forest Algorithm
Random Forest Algorithm Table Of Contents: What Is Random Forest Algorithm? Working Principle Of Random Forest Algorithm. Essential Features Of Random Forest. Important Hyperparameters In Random Forest Algorithm. Difference Between Random Forest And Decision Tree. Advantages and Disadvantages Of Random Forest Algorithm. (1) What Is Random Forest Algorithm? The Random Forest algorithm is an ensemble learning method that combines multiple decision trees to create a robust and accurate predictive model. Random forest is a Supervised Machine Learning Algorithm that is used widely in Classification and Regression problems. (2) How Random Forest Algorithm Works? Step-1: Ensemble of Decision Trees: Random Forest builds an ensemble of
