-

Pruning In Decision Tree ?
Pruning In Decision Tree (1) What Is Pruning? Pruning is a technique used in decision trees to reduce overfitting and improve the generalization ability of the model. It involves removing branches or nodes from the tree that do not contribute significantly to its predictive accuracy. Pruning helps simplify the tree structure, making it less complex and easier to interpret. There are two main types of pruning techniques: (2) Types Of Pruning. Pre Pruning: Pre-pruning involves stopping the growth of the decision tree before it becomes fully expanded. It applies stopping criteria during the construction process to determine when to stop
-
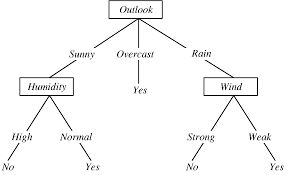
When To Stop Decision Tree Splitting?
When To Stop Decision Tree Splitting? Determining when to stop the splitting process in a decision tree is crucial to prevent overfitting or excessive complexity. Here are some common stopping criteria used in decision tree algorithms: Maximum Depth: The decision tree is limited to a maximum depth or number of levels. Once the tree reaches this depth, no further splitting is performed. Limiting the depth helps control the complexity of the tree and prevents overfitting, particularly when dealing with noisy or small datasets. Minimum Number of Samples per Leaf: Nodes are not allowed to split further if the number of
-

CART, C4.5, ID3 Algorithms
CART, C4.5, ID3 Algorithms CART: CART (Classification and Regression Trees). CART is a versatile algorithm that can be used for both classification and regression tasks. It constructs binary decision trees, where each internal node represents a splitting criterion on a feature, and each leaf node represents a class label or a regression value. The splitting criterion in CART is determined by optimizing a cost function, such as the Gini index for classification or the mean squared error for regression. The algorithm recursively partitions the data based on the selected feature and splits, creating branches until a stopping condition is met.
-

Entropy Vs. Gini Index
Entropy Vs. Gini Index (1) Difference In Entropy & Gini Index. Gini Index: It is the probability of misclassifying a randomly chosen element in a set. The range of the Gini index is [0, 1], where 0 indicates perfect purity and 1 indicates maximum impurity. The Gini index is a linear measure. It can be interpreted as the expected error rate in a classifier. It is sensitive to the distribution of classes in a set. The computational complexity of the Gini index is O(c). It is less robust than entropy. It is sensitive. Formula for the Gini index is Gini(P)
-
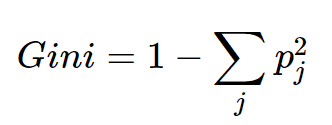
Gini Index In Decision Tree.
GINI Index In Decision Tree Table Of Contents: What Is the GINI Index? Interpreting GINI Index. Example Of GINI Index. What Is the GINI Coefficient? (1) What Is GINI Index? The Gini index, also known as the Gini impurity, is a measure used in decision tree algorithms to quantify the impurity or randomness of a set of examples within a particular node. It is an alternative criterion, alongside entropy, for determining the best feature to split the data. The Gini index is calculated based on the distribution of class labels within a node. It measures the probability of incorrectly classifying
-
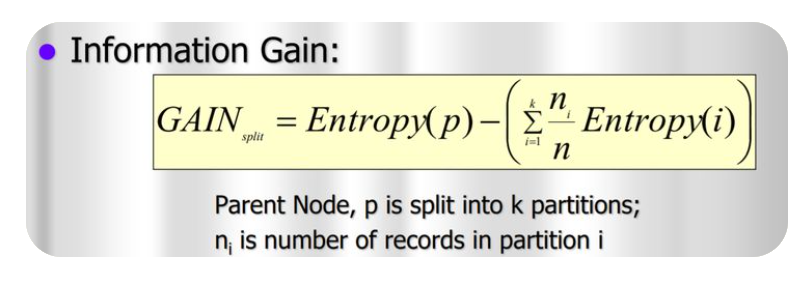
Information Gain In Decision Tree.
Information Gain Table Of Contents: What Is Information Gain? Example Of Information Gain. (1) What Is Information Gain? Information gain is a measure used in decision tree algorithms to determine the best feature to split the data. It quantifies how much information a particular feature contributes to reducing the entropy or impurity within a node. The information gain is calculated by comparing the entropy of the parent node (before the split) with the weighted average of the entropies of the child nodes (after the split), considering each possible outcome of the feature being evaluated. A higher information gain indicates that
-

Entropy In Decision Tree .
Entropy In Decision Tree Table Of Contents: What Is Entropy? Interpreting Entropy. Formula For Entropy. How Decision Tree Uses Entropy? Example Of Entropy Calculation. (1) What Is Entropy? Entropy is a concept used in the context of decision trees to measure the impurity or randomness of a set of examples within a particular node. In Decision Tree algorithms, Entropy is used as a criterion to determine the best feature for splitting the data. In the context of decision trees, entropy is calculated based on the distribution of class labels within a node. If a node contains only examples from a
-

Decision Tree Algorithm.
Decision Tree Algorithm! Table Of Contents: Decision Tree Algorithm. Why Use Decision Trees? Types Of Decision Trees. Terminology Related To Decision Tree. Examples Of Decision Tree. Assumptions While Creating Decision Tree. How Decision Trees Work. Attribute Selection Measures. Advantages & Disadvantages Of Decision Tree. (1) What Is Decision Tree Algorithm? A decision tree is a non-parametric supervised learning algorithm for classification and regression tasks. It has a hierarchical tree structure consisting of a root node, branches, internal nodes, and leaf nodes. Decision trees are used for classification and regression tasks, providing easy-to-understand models. In a Decision tree, there are two nodes,
-
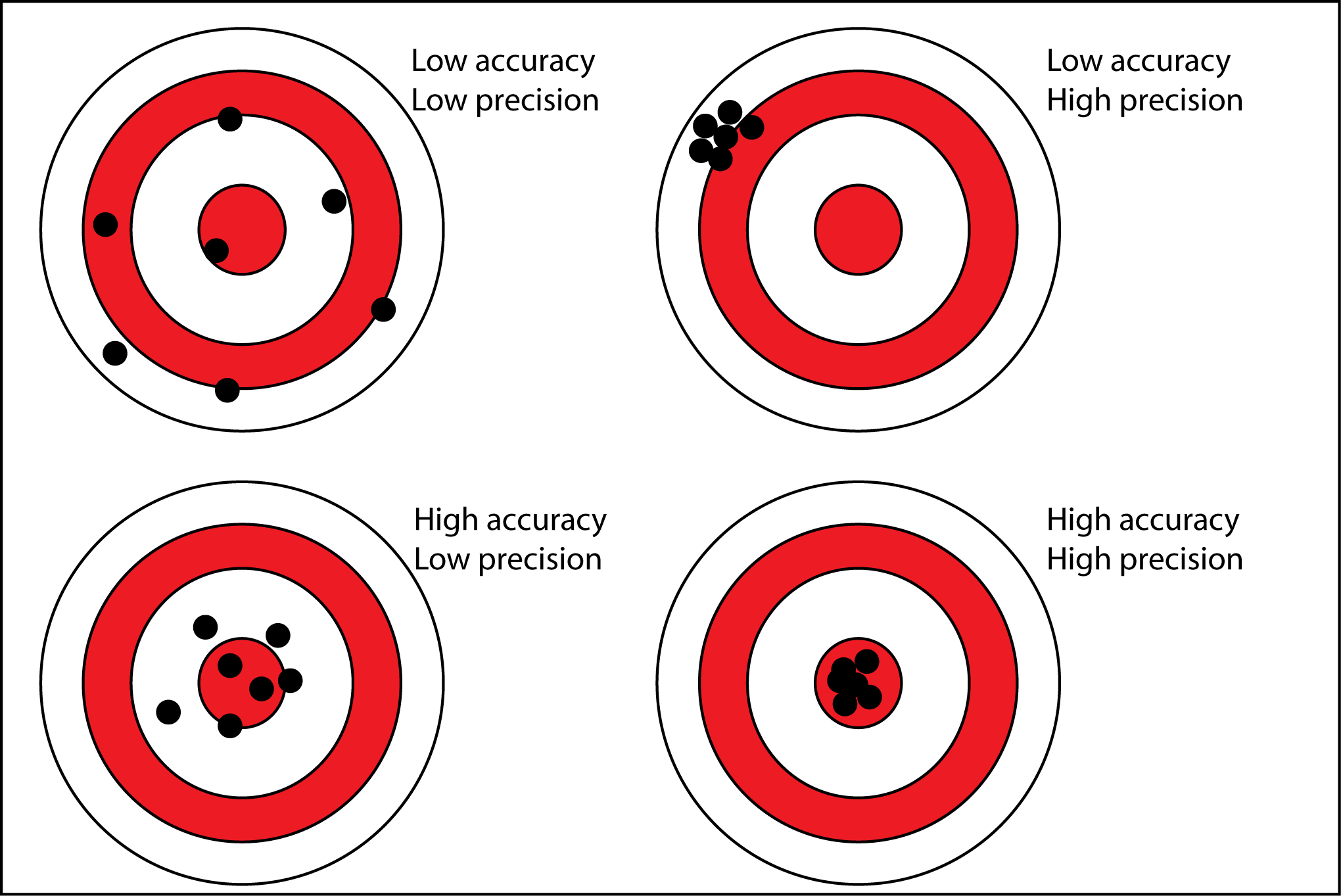
Binary Class Evaluation Metrices.
Evaluation Matrixes Table Of Contents: Accuracy Precision Recall (TPR, Sensitivity) Specificity (TNR) F1-Score FPR (Type I Error) FNR (Type II Error) (1) Accuracy: Accuracy simply measures how often the classifier makes the correct prediction. It’s the ratio between the number of correct predictions and the total number of predictions. The accuracy metric is not suited for imbalanced classes. Accuracy has its own disadvantages, for imbalanced data, when the model predicts that each point belongs to the majority class label, the accuracy will be high. But, the model is not accurate. It is a measure of correctness that is achieved in true prediction. In simple words, it tells us how many predictions are actually positive out
-
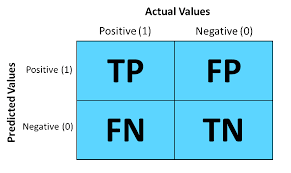
Confusion Metrix
Confusion Metrix Table Of Contents: What Is Confusion Metrix? Why We Need Confusion Metrix? Elements Of Confusion Metrix. Examples Of Confusion Metrix. Evaluation Matrixes. (1) Why We Need Confusion Metrix? In machine learning, Classification is used to split data into categories. But after cleaning and preprocessing the data and training our model, how do we know if our classification model performs well? That is where a confusion matrix comes into the picture. A confusion matrix is used to measure the performance of a classifier in depth. (2) What Is Confusion Metrix? A confusion matrix, also known as an error matrix,
