AWS Global Infrastructure
Table Of Contents:
- What Is AWS Global Infrastructure?
- What Is AWS Region?
- What Is AWS Availability Zone ?
- Edge Locations & AWS Global Network.
- AWS Wavelength (For 5G Applications)
(1) What Is AWS Global Infrastructure?
- AWS Global Infrastructure refers to the physical and network components that power Amazon Web Services (AWS).
- It is designed to provide high availability, scalability, security, and low-latency performance for businesses worldwide.
(2) What Is AWS Region ?
An AWS Region is a geographically isolated area where AWS hosts cloud infrastructure.
Each region consists of multiple data centers (called Availability Zones) to provide high availability, fault tolerance, and scalability.
AWS Regions allow customers to deploy applications closer to their users, reducing latency and ensuring compliance with data regulations.

(2.1) Key Features of AWS Regions.





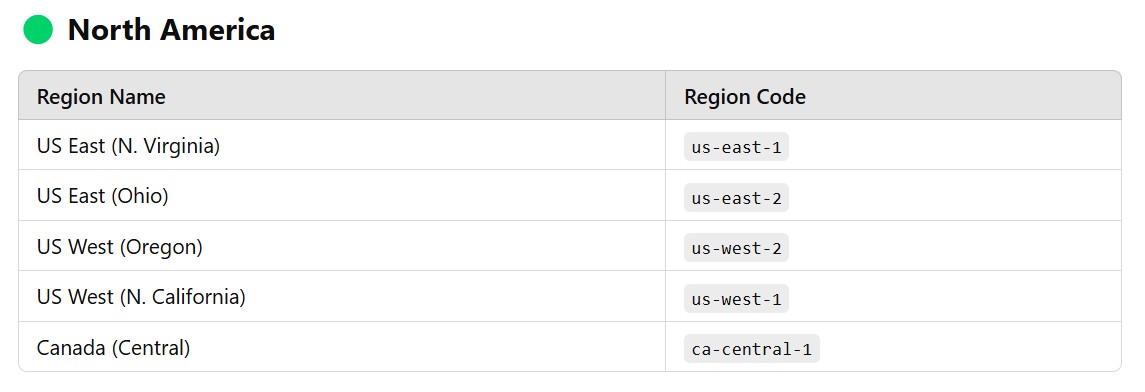
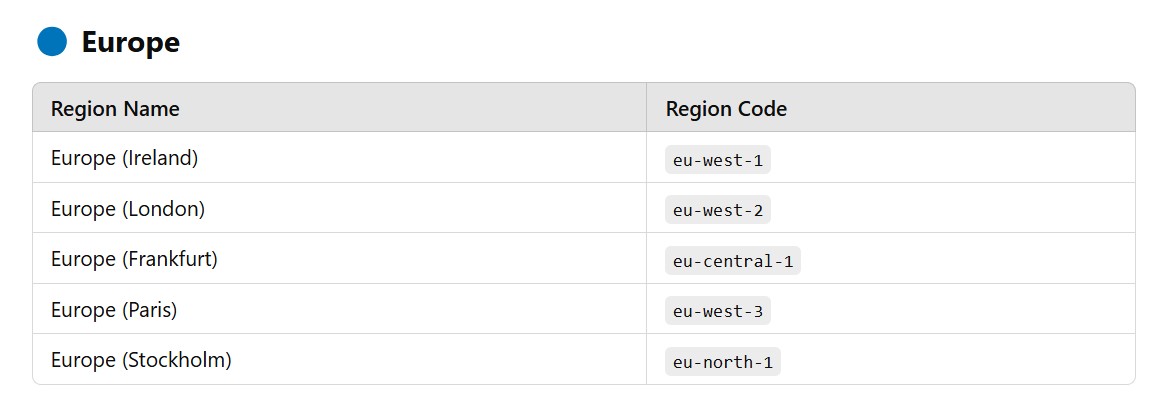
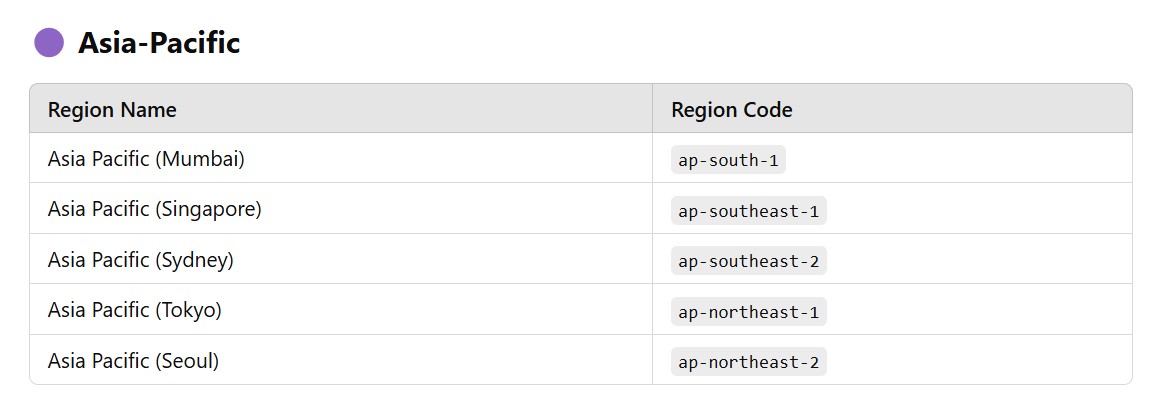
(2.2) AWS Regions List (2025)
- AWS currently has 32+ regions and over 100+ Availability Zones worldwide.

(2.3) How To Choose Right Region?





(2.4) FAQ

(3) What Is AWS Availability Zone ?
An Availability Zone (AZ) is a physically separate data center within an AWS Region that is designed to be fault-tolerant and highly available.
Each AWS Region consists of multiple AZs, which are connected by low-latency, high-speed networks to ensure reliability, scalability, and disaster recovery.
(3.1) Key Features of Availability Zones
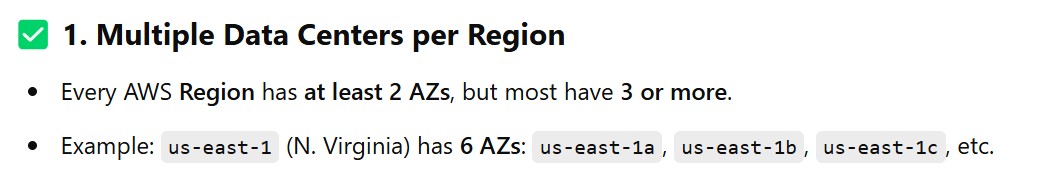



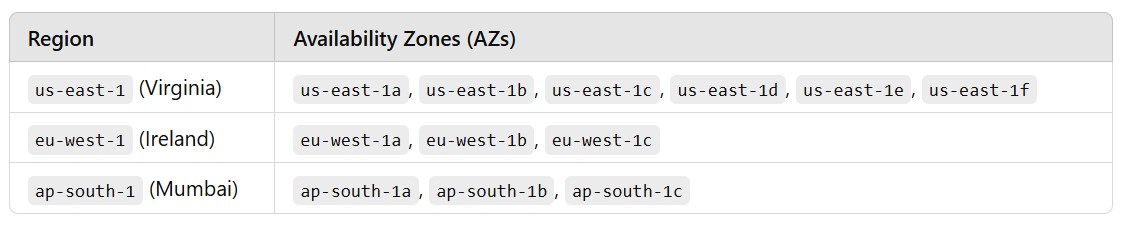
(3.2) Example of AZs in a Region
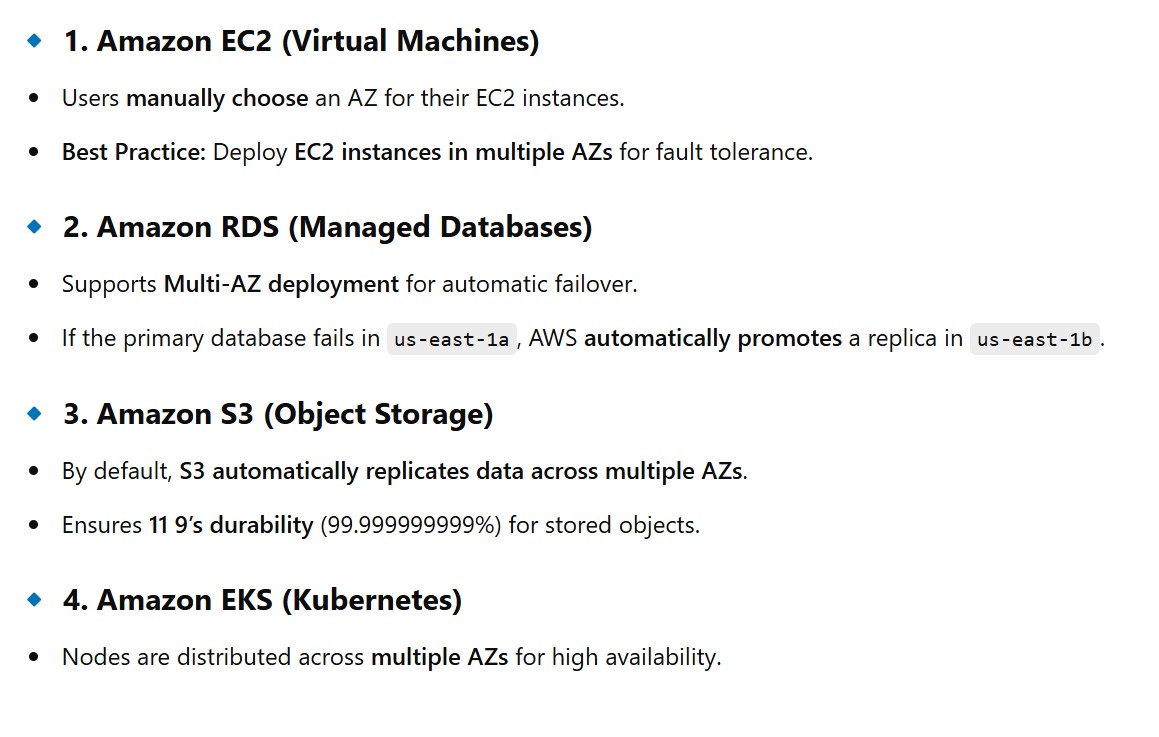
(3.3) How AWS Services Use AZs
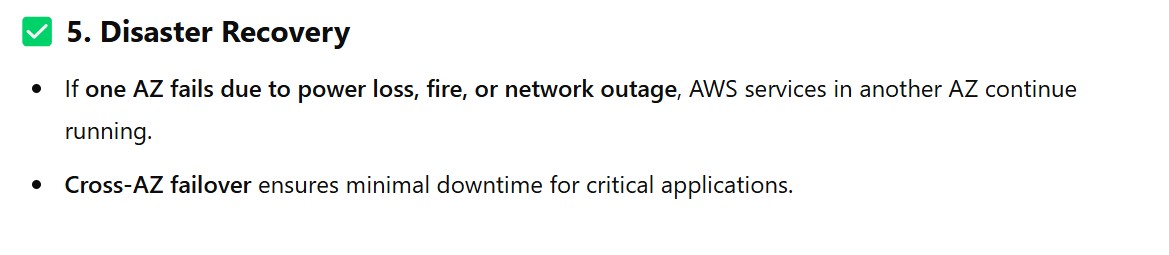
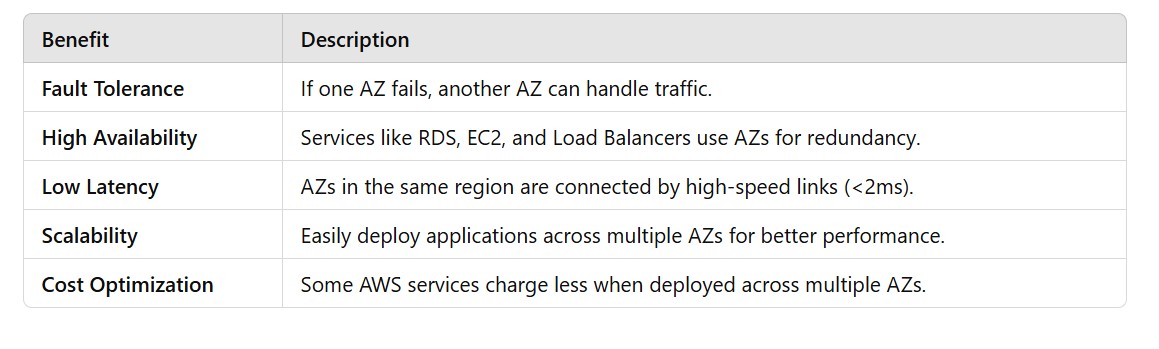
(3.4) Benefits of Using Multiple AZs
(3.5) FAQ

(3) Edge Locations & AWS Global Network

(4) AWS Local Zones

(5) AWS Wavelength (For 5G Applications)

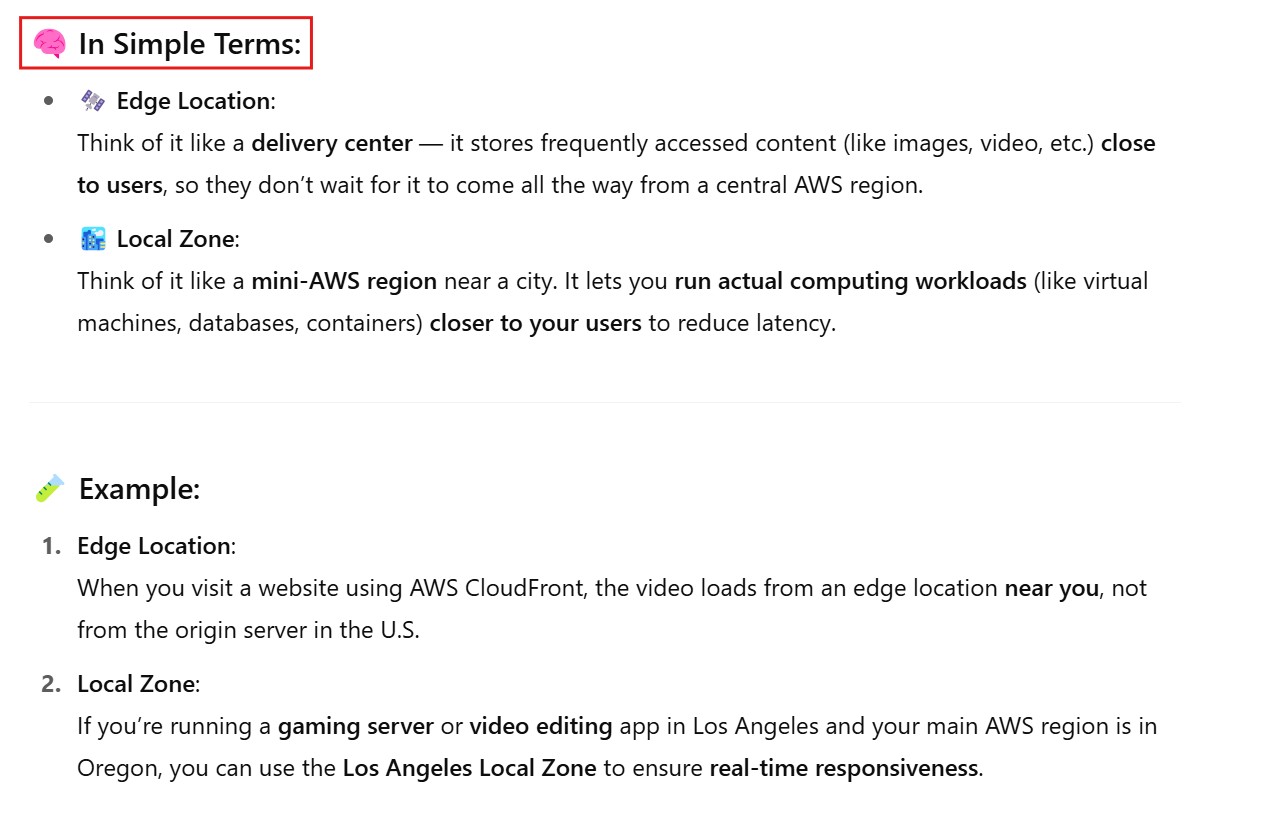
(6) AWS Edge Location Vs. Local Zone.