-
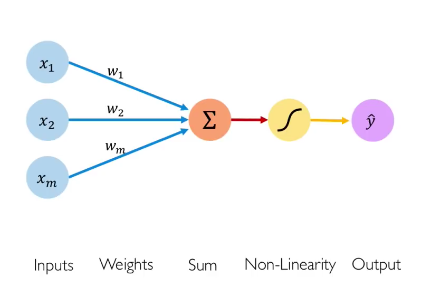
Working Of A Single Neuron.
Working Of A Single Neuron. Table Of Contents: The Linear Unit. Example: The Linear Unit As A Model. Multiple Inputs. (1) The Linear Unit. So let’s begin with the fundamental component of a neural network: the individual neuron. As a diagram, a neuron (or unit) with one input looks like below: The input is x. Its connection to the neuron has a weight which is w. Whenever a value flows through a connection, you multiply the value by the connection’s weight. For the input, what reaches the neuron is w * x. A neural network “learns” by modifying its weights. The b is a special kind of weight we call
-
How Do Neural Networks Work?
How Does Neural Networks Works? Table Of Contents: How Does Neural Networks Work? Input Data. Feedforward. Activation Functions. Output Layer. Loss Function. Backpropagation and Training. Training Iterations. Prediction and Inference. (1) How Does Neural Networks Work? Neural networks work by processing input data through a network of interconnected artificial neurons, also known as nodes or units. The network learns from the input data and adjusts the connections (weights) between neurons to make accurate predictions or perform specific tasks. Here’s a general overview of how neural networks work: (2) Input Data. The neural network receives input data, which can be in
-
What Are Neural Networks?
What Are Neural Networks? Table Of Contents: Neural Networks? What Are Neurons? What Are Layers? Weights & Biases. Activation Functions. Feedforward and Backpropagation. Deep Neural Networks. (1) Neural Networks? Neural networks, also known as artificial neural networks (ANNs), are computational models inspired by the structure and functioning of the human brain’s neural networks. They consist of interconnected artificial neurons, also called nodes or units, organized in layers. (2) What Are Neurons? Neurons are the basic building blocks of neural networks. Artificial neurons receive input signals, perform computations, and produce an output signal. Each neuron applies an activation function to the
-

Introduction To Deep Learning.
Introduction To Deep Learning Table Of Contents: What Is Deep Learning? Applications Of Deep Learning. Importance Of Deep Learning. History Of Deep Learning. What Are Neural Networks? How Do Neural Networks Work? (1) What Is Deep Learning ? Deep learning is a subfield of machine learning and artificial intelligence (AI) that focuses on training artificial neural networks to learn and make intelligent decisions. It is characterized by the use of deep neural networks, which are neural networks with multiple layers of interconnected artificial neurons. In deep learning, the term “deep” refers to the depth of the neural networks, meaning they
-

Deep Learning Syllabus
Deep Learning Syllabus (1) Introduction To Deep Learning: Overview of deep learning and its applications. Historical development and milestones in deep learning. Basics of neural networks and their components. (2) Artificial Neural Networks: Perceptrons and activation functions Feedforward neural networks Training algorithms: gradient descent, backpropagation Regularization techniques: dropout, weight decay Optimization algorithms: stochastic gradient descent, Adam Initialization strategies (3) Convolutional Neural Networks (CNNs): Introduction to CNNs and their architecture. Convolutional layers, pooling layers, and fully connected layers CNN training and optimization CNN applications in computer vision tasks (e.g., image classification, object detection) (4) Recurrent Neural Networks (RNNs): Introduction to RNNs
-

Deep Learning Tutorials
Deep Learning Syllabus admin March 18, 2024 Deep Learning Tutorials Read More
