Deep Learning – What Is Early Stopping ?
Table Of Contents:
- What Is Early Stopping ?
- Why Is Early Stopping Is Needed ?
- How Early Stopping Works ?
- Benefits Of Early Stopping .
- Visual Representation.
- Hyperparameter : Patience .
(1) What Is Early Stopping ?

(2) Why Is Early Stopping Needed ?

(3) How Early Stopping Works ?

(4) Benefits of Early Stopping .

(5) Visual Representation .

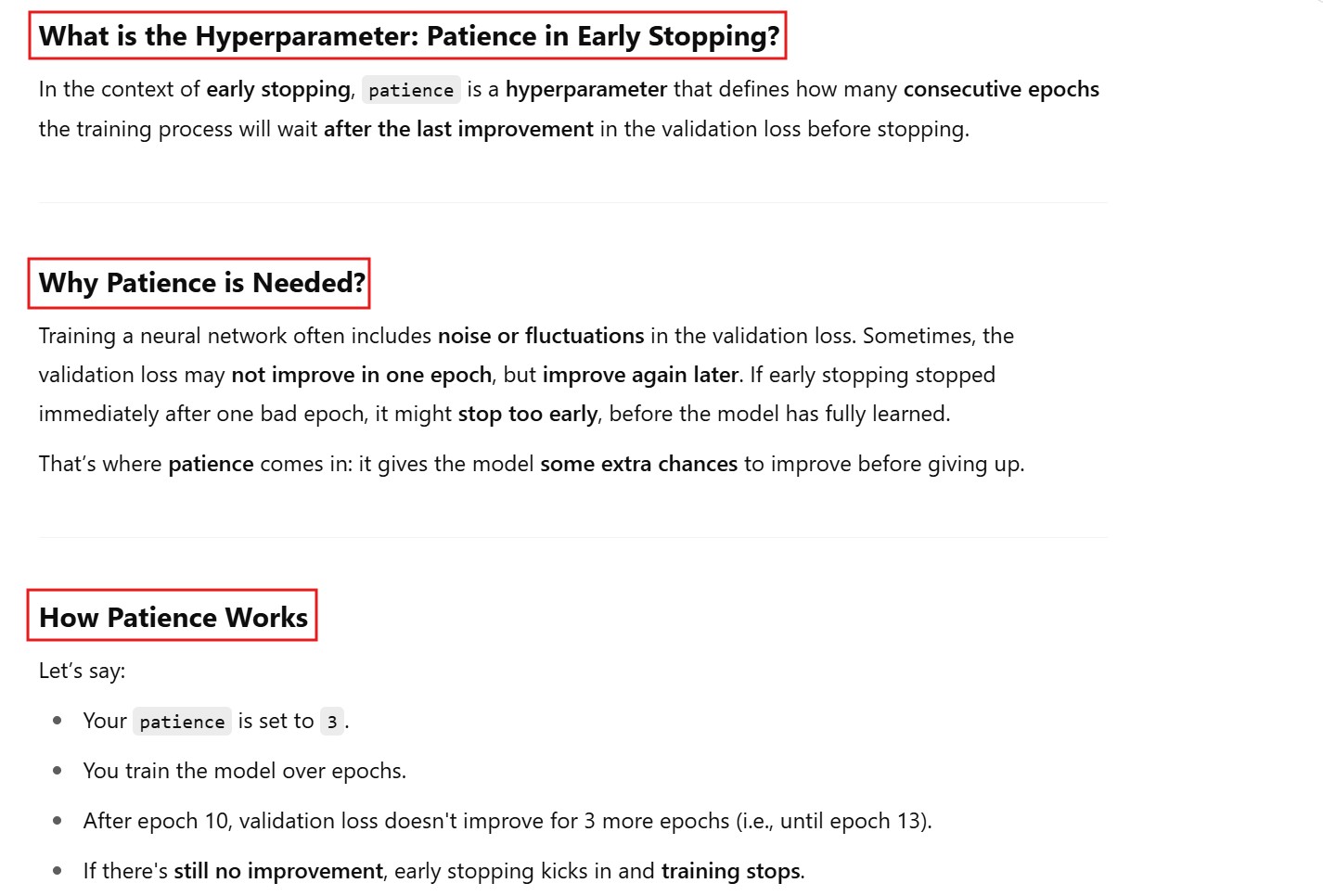
(6) Hyperparameter: Patience

(7) Implementation in Keras (TensorFlow)
from tensorflow.keras.models import Sequential
from tensorflow.keras.layers import Dense
from tensorflow.keras.callbacks import EarlyStopping
# 1. Build the model
model = Sequential([
Dense(128, activation='relu', input_shape=(input_dim,)),
Dense(64, activation='relu'),
Dense(1, activation='sigmoid') # for binary classification
])
model.compile(optimizer='adam', loss='binary_crossentropy', metrics=['accuracy'])
# 2. Define EarlyStopping callback
early_stop = EarlyStopping(
monitor='val_loss', # What to monitor
patience=3, # Number of epochs to wait after no improvement
restore_best_weights=True # Restore best weights after stopping
)
# 3. Fit the model with validation data
history = model.fit(
X_train, y_train,
validation_data=(X_val, y_val),
epochs=100,
callbacks=[early_stop], # Add callback here
batch_size=32
)


