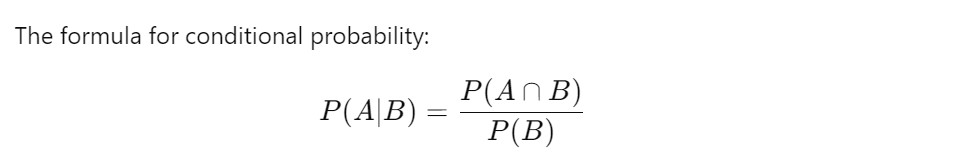Probability Theory
Table Of Contents:
- Probability Of ‘A’ and ‘B’ Happening Together.
- Probability Of ‘A’ Given ‘B’ has already Happened.
(1) Probability Of ‘A’ and ‘B’ Happening Together.
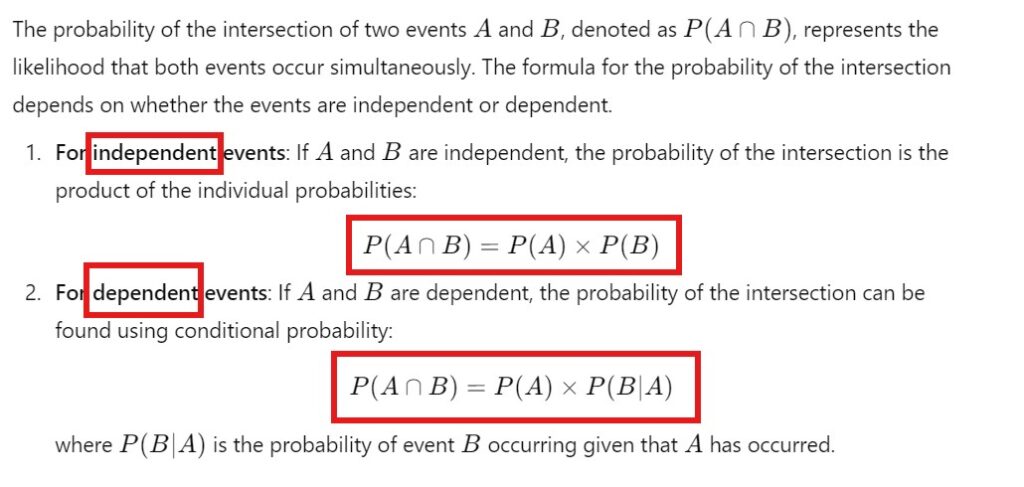
P(A∩B)=P(A)×P(B) for an independent event if there is no relationship between a and b how we are multiplying there individual probability
- As here we are considering two events we need to consider all possible outcomes for both the events.
- For rolling two dies together we will have 36 number of outcomes.
- For tossing two coins together we will hae 4 possible outcomes.


(2) Probability Of ‘A’ Given ‘B’ Has Already Happened.