GenAI – Delimiter Based Chunking
Table Of Contents:
- What Is Delimiter Based Chunking ?
- Examples Of Delimiters.
- When To Use Delimiter Based Chunking ?
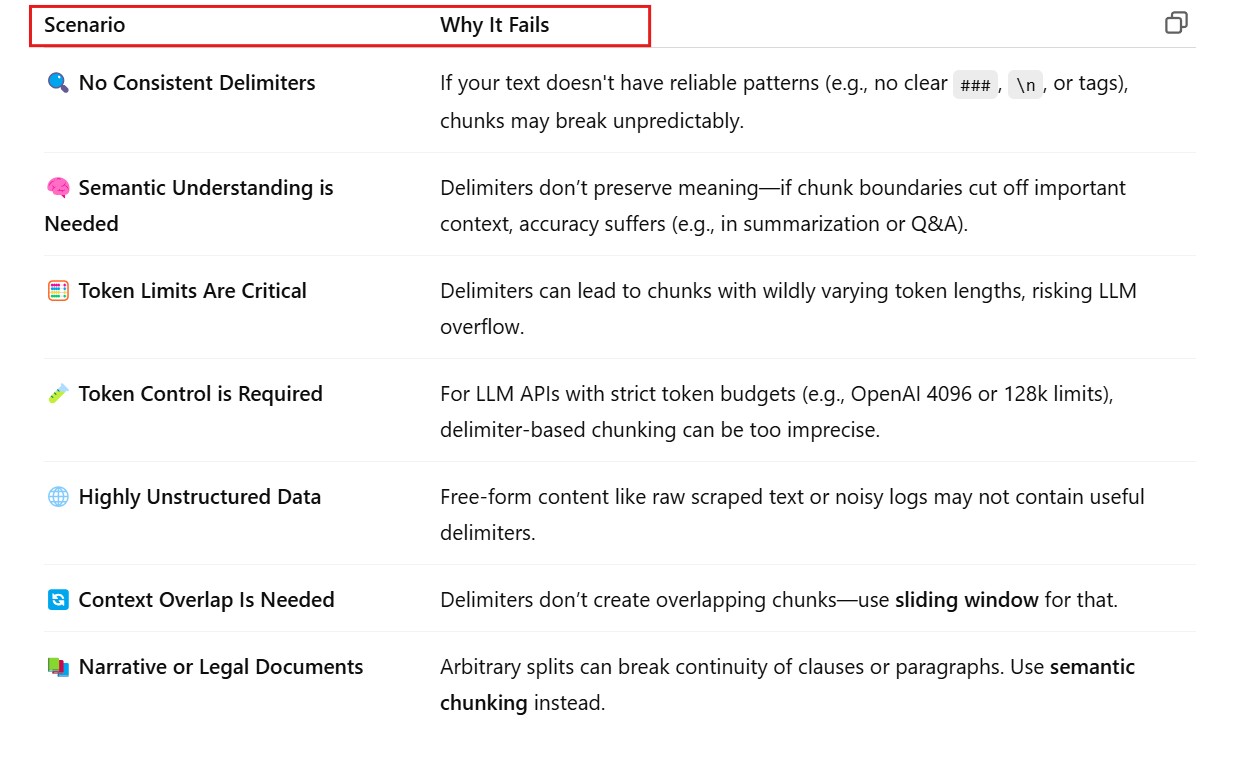
- When Not To Use Delimiter Based Chunking ?
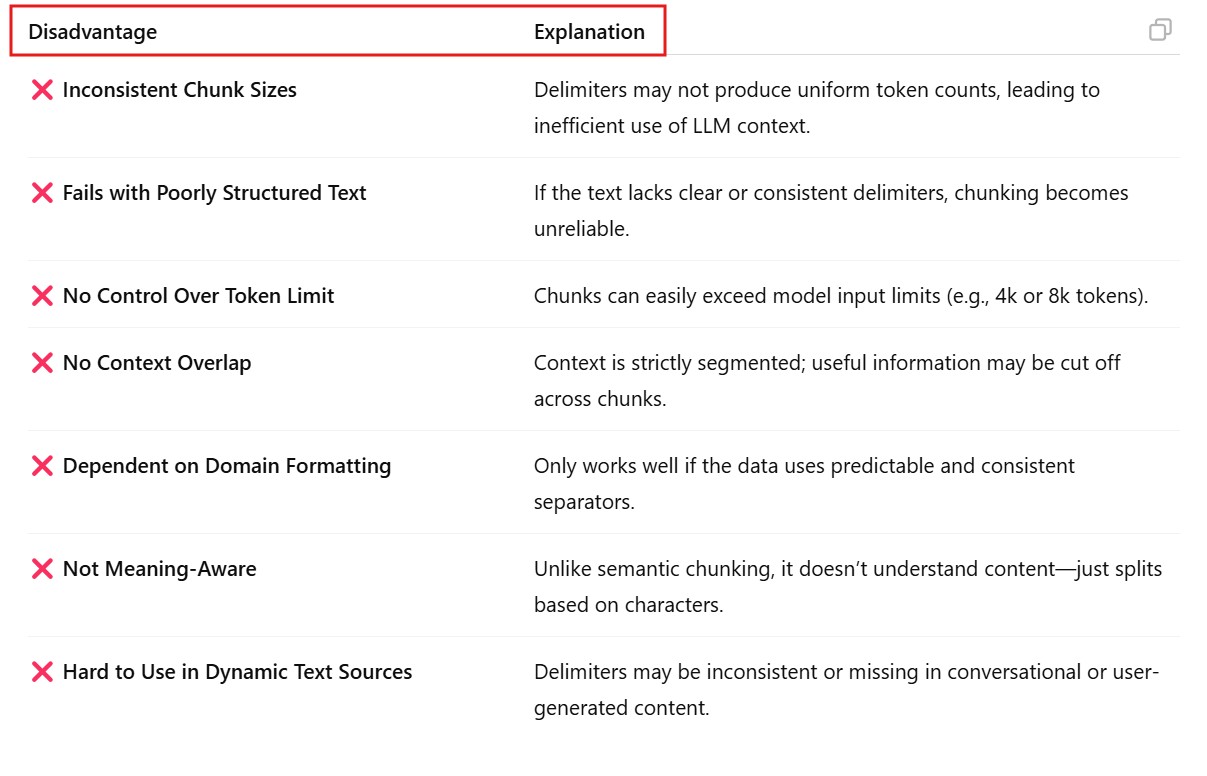
- Advantages Of Delimiter Based Chunking.
- Disadvantages Of Delimiter Based Chunking.
- Examples Of Delimiter Based Chunking.
(1) What Is Delimiter Based Chunking ?



(2) Examples Of Delimiter.
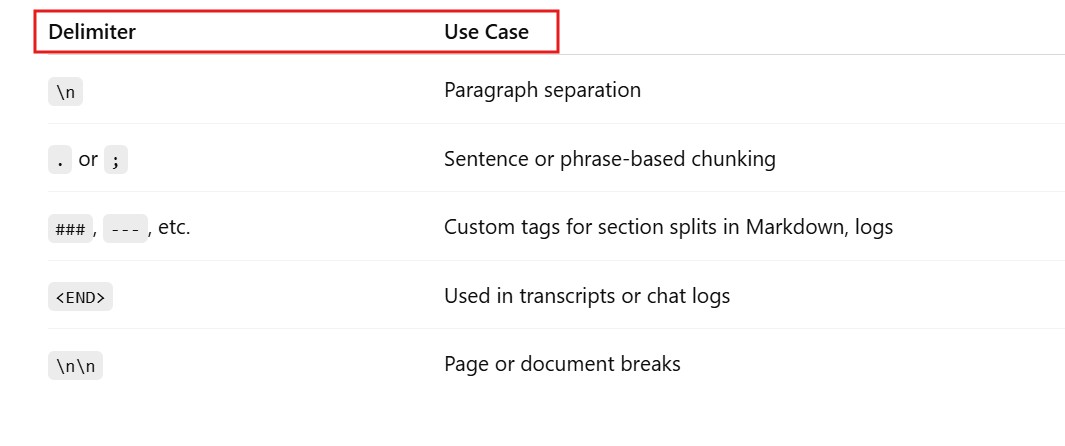
(3) When To Use Delimiter Based Chunking ?


(4) When Not To Use Delimiter Based Chunking ?
(5) Advantages Of Delimiter Based Chunking .

(6) Disadvantages Of Delimiter Based Chunking .
(7) Examples Of Delimiter Based Chunking .
Example 1: Chunking Markdown Sections
text = """
# Introduction
This is the introduction section.
# Methods
This section discusses methods.
# Conclusion
This is the conclusion.
"""
# Chunk using "#" as the delimiter
chunks = text.split("# ")
chunks = [chunk.strip() for chunk in chunks if chunk.strip()]
for i, chunk in enumerate(chunks):
print(f"Chunk {i+1}:\n{chunk}\n")

Example 2: Chunking Chat Transcripts
chat_log = "User: Hi\nBot: Hello!\nUser: What’s the weather?\nBot: It's sunny today."
# Split by newline to separate turns
chunks = chat_log.split('\n')
for i, chunk in enumerate(chunks):
print(f"Turn {i+1}: {chunk}")

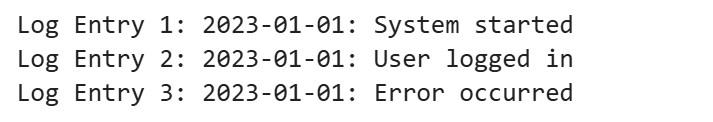
Example 3: Chunking Logs or CSV Rows
log_text = """2023-01-01: System started
2023-01-01: User logged in
2023-01-01: Error occurred"""
# Split each log entry using newline
chunks = log_text.split('\n')
for i, chunk in enumerate(chunks):
print(f"Log Entry {i+1}: {chunk}")
Example 4: Custom Delimiter (=== END ===)
data = "Q1: What is AI?\nAnswer: ...=== END ===Q2: What is ML?\nAnswer: ..."
# Use custom delimiter
chunks = data.split("=== END ===")
for i, chunk in enumerate(chunks):
print(f"Question {i+1}:\n{chunk.strip()}\n")


