Linear Regression – Assumption- 1 (Linear Relationship)
Table Of Contents:
- What Is Q – Q Plot ?
- Example Of Q – Q Plot .
- Why There Is A Straight Line In The Q – Q Plot ?
(1) What Is Q – Q Plot ?
A Q–Q plot (Quantile–Quantile plot) is a probability plot that compares the quantiles of a dataset to the quantiles of a theoretical distribution (often the normal distribution).
It helps to visually check if your data is normally distributed.
(2) When to use a Q–Q Plot ?
To assess normality (Is my data normally distributed?)
To detect skewness, outliers, or distribution mismatches.
(3) Interpreting Q–Q Plot ?

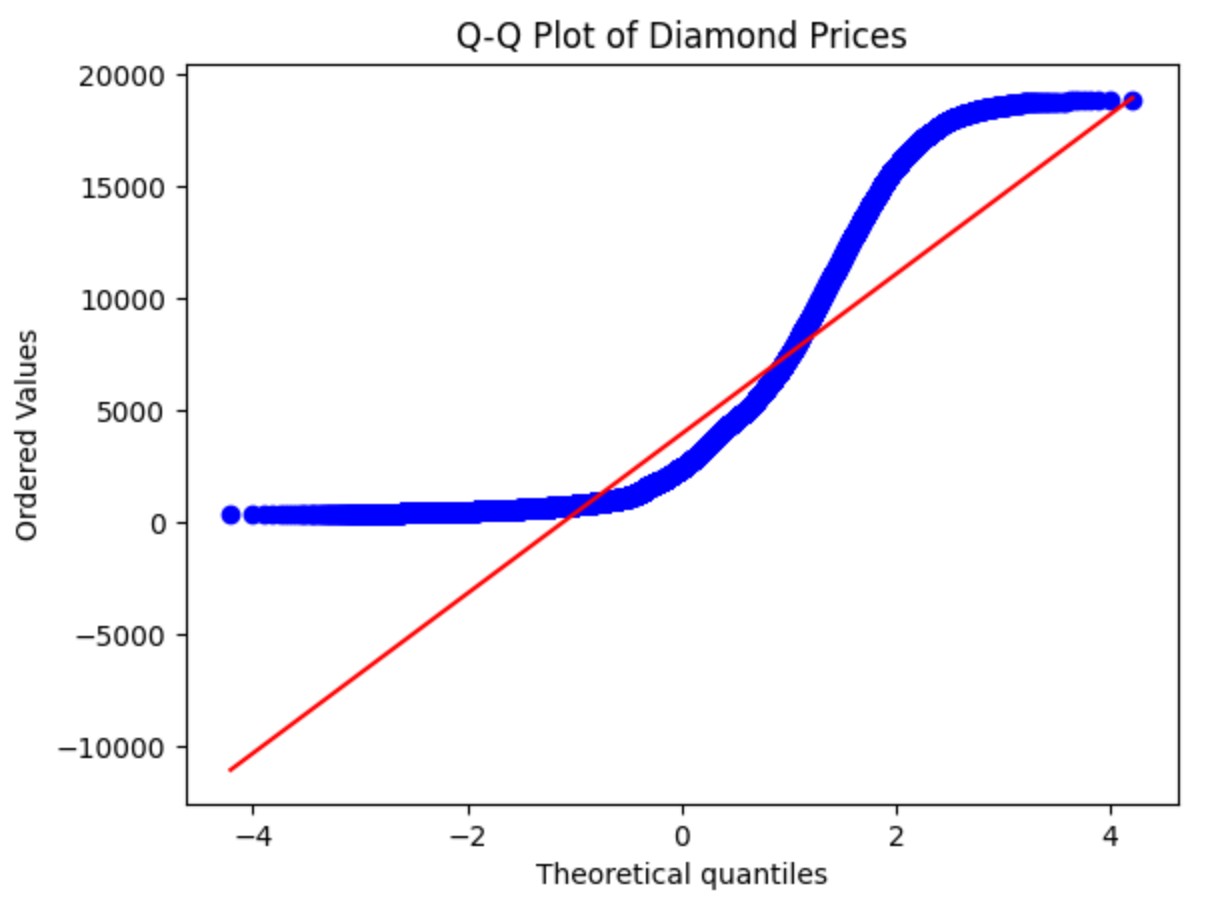
(4) Example Of Q–Q Plot ?
import seaborn as sns
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import scipy.stats as stats
# Load sample data
data = sns.load_dataset("diamonds") # built-in Seaborn dataset
x = data["price"] # taking the 'price' column
# Q-Q plot
stats.probplot(x, dist="norm", plot=plt)
plt.title("Q-Q Plot of Diamond Prices")
plt.show()
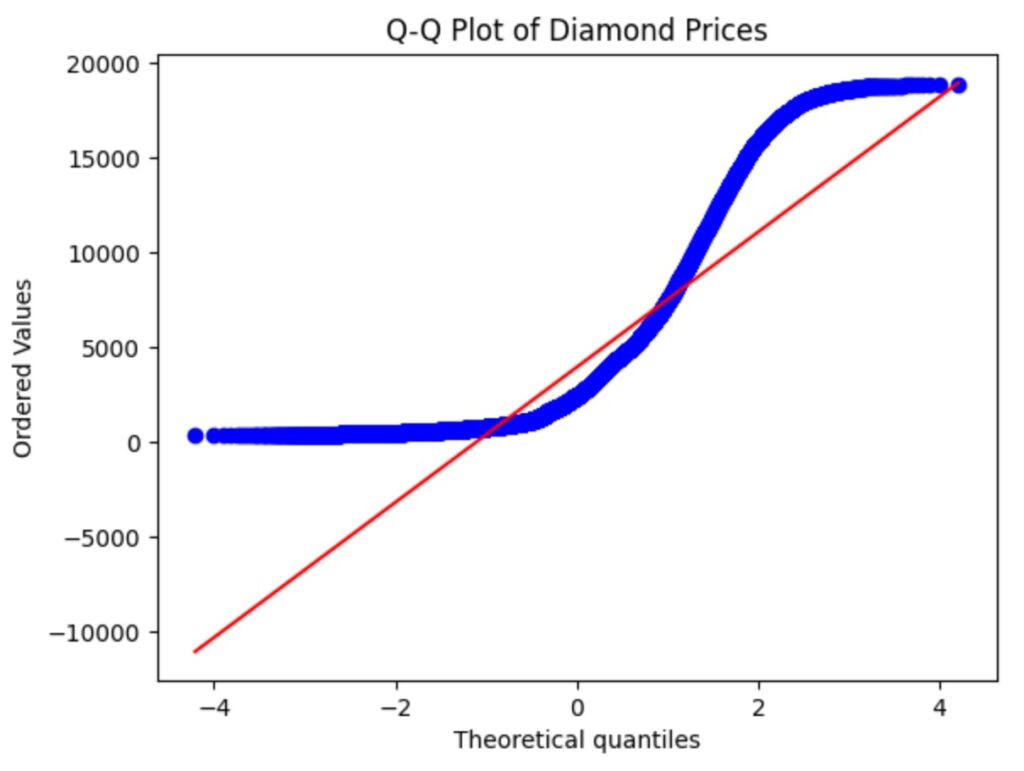

(5) Why There Is A Straight Line In Q – Q Plot ?
- The straight line (also called the reference line or theoretical line) represents the ideal case — what the quantiles of your data would look like if they were perfectly following the specified theoretical distribution (usually the normal distribution).
- The straight line is the ideal condition when your data quantile value matches with the normal distribution quantile value.

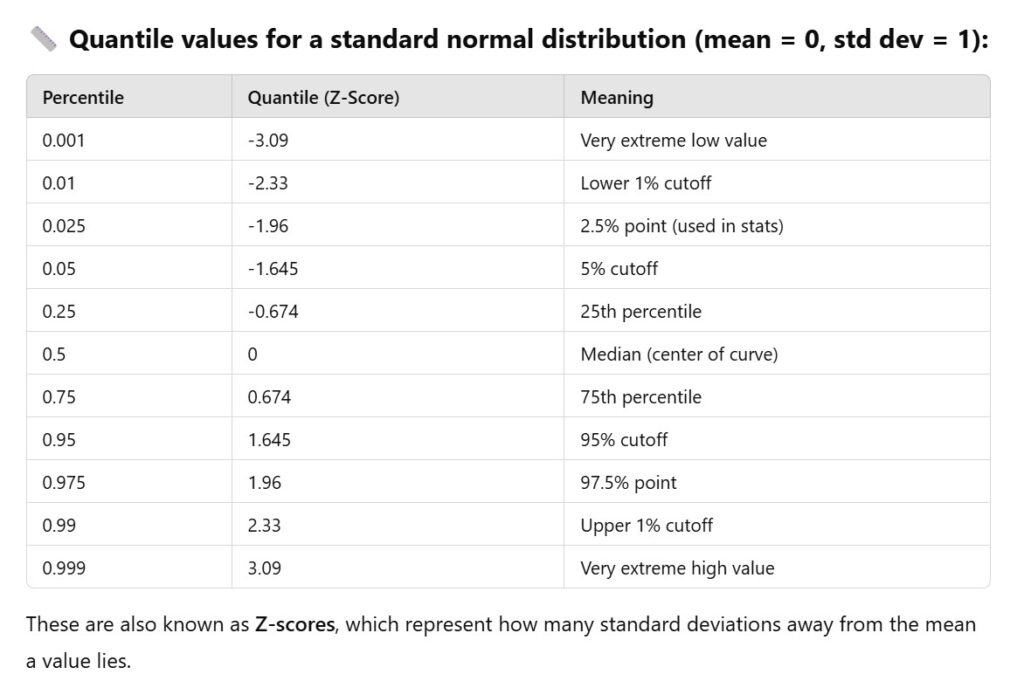
(6) Quantile Values Of The Normal Distribution.