-
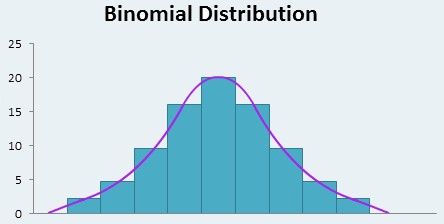
What Is Binomial Distribution?
What Is Binomial Distribution? Table Of Contents: What Is Binomial Distribution? Formula For Binomial Distribution. Diagram For Binomial Distribution. Examples Of Binomial Distribution. (1) What Is Binomial Distribution? The Binomial Distribution is the discrete probability distribution that gives only two possible results in an experiment, either Success or Failure. For example, if we toss a coin, there could be only two possible outcomes: heads or tails, and if any test is taken, then there could be only two results: pass or fail. Binomial Distribution is the extension of Uniform Distribution because in Uniform Distribution you will do the experiment only once and
-
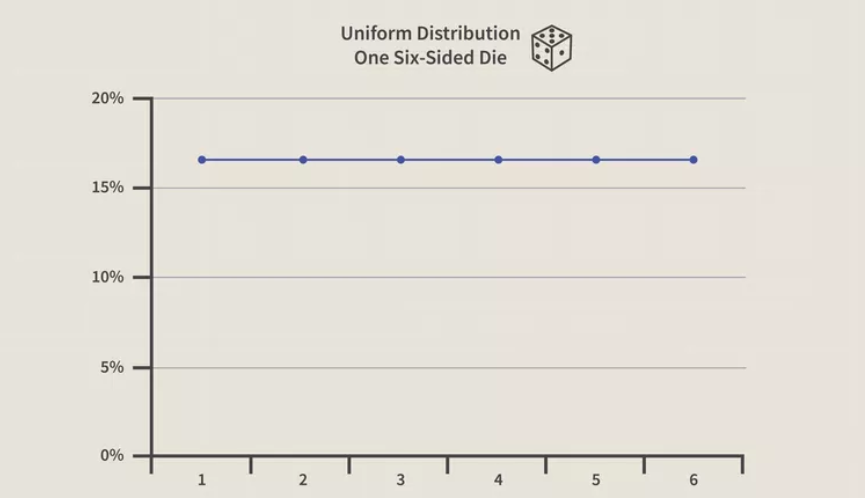
What Is Uniform Distribution?
What Is Uniform Distribution? Table Of Content: What Is Uniform Distribution? Formula For Uniform Distribution. Example Of Uniform Distribution. (1) What Is Uniform Distribution? In statistics, uniform distribution refers to a type of probability distribution in which all outcomes are equally likely. A deck of cards has within it uniform distributions because the likelihood of drawing a heart, a club, a diamond, or a spade is equally likely. A coin also has a uniform distribution because the probability of getting either heads or tails in a coin toss is the same. The uniform distribution can be visualized as a straight horizontal line, so for
-
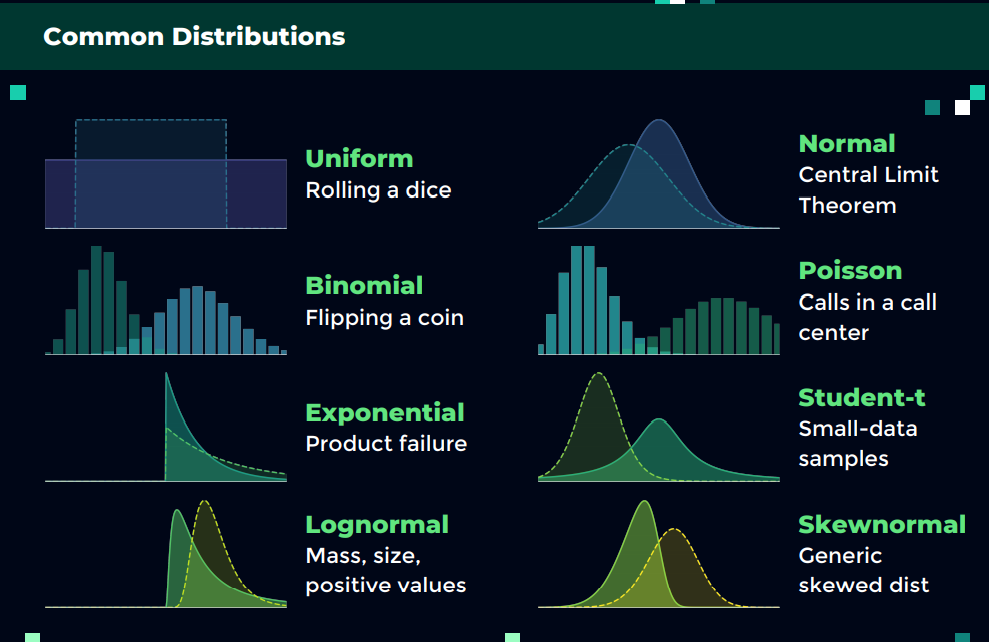
What Is Statistical Distribution ?
What Is Statistical Distribution? Table Of Contents: What Is Statistical Distribution? Why It Is Important? Types Of Statistical Distributions. (1) What Is Statistical Distribution? A data distribution is a function or a listing that shows all the possible values (or intervals) of the data. Often, the data in a distribution will be ordered from smallest to largest, and graphs and charts allow you to easily see both the values and the frequency with which they appear. This distribution describes the grouping or the density of the observations, called the probability density function. Once you know the data distribution you can calculate the probability of
-
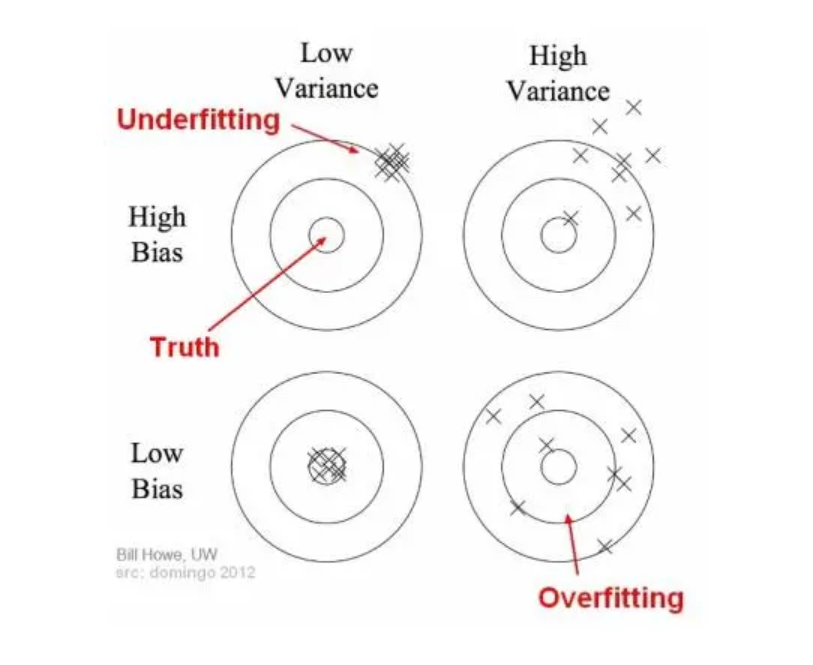
What Is Bias & Variance Tradeoff?
What Is Bias & Variance Tradeoff? Table Of Contents: What Is Bias & Variance? Problem With High Bias & High Variance. Way To Reduce High Bias & Variance. What Is Bias & Variance Tradeoff? (1) What Is Bias & Variance ? Bias: Bias in collecting sample data set refers to the tendency of inclining towards particular group or community based on the preference of data collector. High bias in the data set will not accurately represents the entire population. Hence your statistical analysis will be wrong about the population. Variance: Variance in the sample dataset refers to, how far the
-
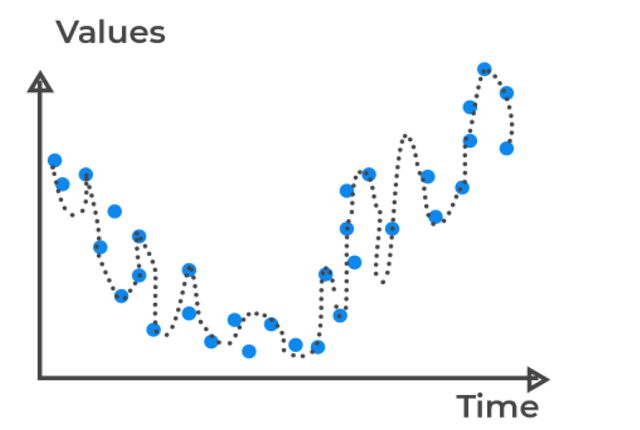
What Is Variance In Statistics ?
What Is Variance In Statistics? Table Of Contents: What Is Variance? Examples Of Variance. How To Calculate Variance? Advantages & Disadvantages Of Variance. Why Does Variance Matters? (1) What Is Variance ? Variance refers to how the individual data points vary from each other in a sample dataset. It is the statistical measurement of the spread between numbers in a data set. More specifically, variance measures how far each number in the set is from the mean (average), and thus from every other number in the set. Variance is often depicted by this symbol: σ2. (2) Examples Of Variance ? Example-1 When
-
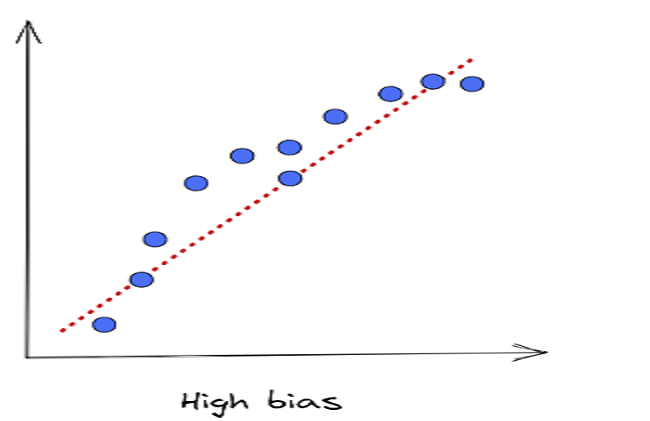
What Is Bias In Statistics?
What Is Bias In Statistics? Table Of Contents: What Is Bias? How To Calculate Bias? Types Of Bias. Examples Of Bias. How To Avoid Sampling Bias. (1) What Is Bias ? Bias refers to the inclination for or against one person or group, especially in a way considered to be unfair. Bias refers to the flaw in the experiment design or data collection process, which generates results that don’t accurately represent the population. Bias mainly occurs due to human action, if you can control the human factor in your experiment, you can reduce the ‘Bias’. (2) How To Calculate Bias
-

Q & A – Pandas Advance Interview Questions
(1) Difference Between “apply()” and “applymap()” Method In Pandas. Main difference between “apply()” and “applymap()” is that, “apply()” method applies the function entirely by taking a row or column as an argument. “applymap()” method applies the function elementwise to each row or each column. Example import pandas as pd df1 = pd.DataFrame({‘names’: [‘Subrat’, ‘Arpita’, ‘Abhispa’, ‘Subhada’, ‘Sonali’], ‘marks’: [67, 75, 84, 90, 99]}) df1 df1.apply(lambda x:len(x)) Output: Note: Here ‘5’ represents the total elements inside the ‘name’ and ‘marks’ columns. Here apply() considered ‘name’ and ‘column’ as a series and calculated its length. df1.applymap(lambda x: len(str(x))) Output: Note: Here applymap()
-

Q & A – Pandas Basics
(1) What Is Pandas In Python? Pandas is an open-source, python-based library used in data manipulation applications requiring high performance. The name is derived from “Panel Data” having multidimensional data. This was developed in 2008 by Wes McKinney and was developed for data analysis. Pandas are useful in performing 5 major steps of data analysis – Load the data, clean/manipulate it, prepare it, model it, and analyze the data. (2) Define Pandas dataFrame? A data frame is a 2D mutable and tabular structure for representing data labelled with axes – rows and columns. The syntax for creating a data frame:
-

Q & A – Python Advanced
(1) How Are Arguments Passed By Value Or By Reference In python? Pass by value: A copy of the actual object is passed. Changing the value of the copy of the object will not change the value of the original object. Pass by reference: Reference to the actual object is passed. Changing the value of the new object will change the value of the original object. In Python, arguments are passed by reference, i.e., reference to the actual object is passed. Example-1: def appendNumber(array): array.append(4) arr = [1, 2, 3] # Mutable Object print(arr) appendNumber(arr) print(arr) [1, 2, 3] [1,
-

Q & A – Python Miscellaneous.
(1) What is Python? What are the benefits of using Python What Is Python: Python is a high-level, interpreted, general-purpose programming language. Being a general-purpose language, it can be used to build almost any type of application with the right tools/libraries. Additionally, python supports objects, modules, threads, exception-handling, and automatic memory management which help in modelling real-world problems and building applications to solve these problems. Benefits Of Using Python: Python is a general-purpose programming language that has a simple, easy-to-learn syntax that emphasizes readability and therefore reduces the cost of program maintenance. Moreover, the language is capable of scripting, is
