-
GIT – How To Create A GIT Repository ?
How To Create A GIT Repository ? Table Of Contents: Create Your New Project Folder. Initializing The Project Folder With GIT. (1) Creating A New Project Folder Create your project directory where you want to keep all of your project files. (2) Initialize The Folder With GIT You need to initialize your new folder with GIT, so that it will track the history of the files. Go inside the project folder and run the below command. Step-1: Go Inside The Project Folder Step-2: Right Click Inside The Folder and Select GIT Bash Here Step-3: GIT Command Prompt Will Open Step-4:
-
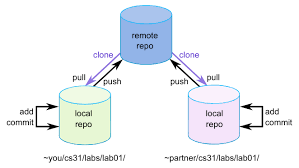
GIT – What Is A GIT Repository ?
What Is A GIT Repository ? Table Of Contents What Is Git Repository ? Types Of Git Repository ? (1) What Is A GIT Repository? A Git repository (repo) is a storage location where all the files, history, and version control information of a project are kept. It helps track changes, collaborate with others, and revert to previous versions when needed. (2) Types Of GIT Repository? There are two types of Git repository. Local Repository Remote Repository (3) Local GIT Repository. Store all the file history, branches and other settings in your local computer. A Git repository is the .git/ folder inside
-

GIT – GIT Environment Setup
GIT Environment Setup Table Of Contents: What Is GIT Environment Setup? Setting Up GIT Environment Variables. (1) What Is GIT Environment Setup ? If you are working with other developers, you need to know who is checking the code in and out, and making the changes. Setting user.name and user. email is the necessary configuration option as your name and email appear in your commit messages. (2) Setting Up GIT Environment Variables. (1) Setting Up Username git config – global user.name 'Subrat@1' (2) Setting Up Email Id git config – global user.email '[email protected]' (3) Setting Colored Output git config – global color.ui true
-

GIT – How To Install GIT ?
How To Install GIT Step-1:Open The GIT Website https://git-scm.com/downloads Step-2: Choose The Type Of Operating System You Have Step-3: Double Click On Git .exe File Step-4: Read The License Agreement And Click On Next Step-5: Select Destination Location Step-6: Keep This As It Is. Step-7: Keep This As It Is Step-8:Keep This As It Is Step-9:Keep This As It Is Step-10:Keep This As It Is Step-11:Keep This As It Is Step-12:Keep This As It Is Step-13:Keep This As It Is Step-14:Keep This As It Is Step-15:Keep This As It Is Step-16:Keep This As It Is Step-17:Keep This As It Is
-

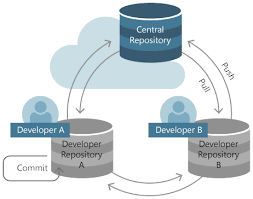
GIT – What Is GIT ?
What Is GIT? Table Of Contents: What Is GIT ? Features Of GIT. GIT Workflow. (1) What Is GIT ? GIT is a Version Control System which will automatically create different versions of your file when you make any changes. It is most widely used for source code management in software development. GIT allows multiple developers to work on a single file and merge the changes at last. It supports non-linear development through its thousands of parallel branches (2) Features Of GIT ? Tracks history Free and open source Supports non-linear development Creates backups Scalable Supports collaboration Branching is easier
-
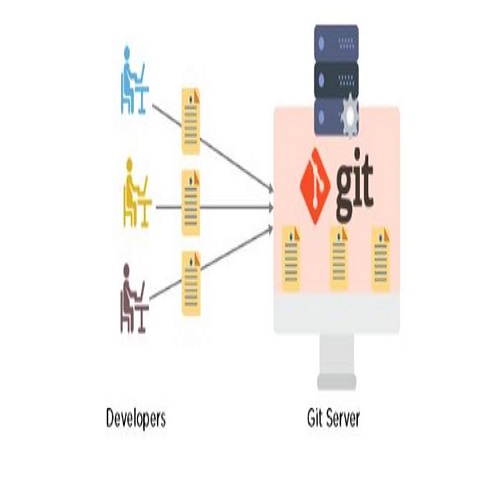
GIT – What Is Version Control ?
What Is Version Control System? Table Of Contents: What Is Version Control System? Benefits Of Version Control Systems (1) What Is Version Control System? Imagine you are working on your project assignment and every day you are adding up something to your project. And you just realized that today you had done something wrong in your project and want to revert it back to the previous day’s work. In this situation, if you have saved your previous day’s work then you can revert back to that. So if you save everyday work in a separate file manually, it will be
-
GIT – Syllabus
(1) What Is Version Control ? (2) Benefits Of Version Control Systems (3) What Is Source Code Management ? (4) What Is GIT ? (5) Why We Need GIT ? (6) How To Install GIT ? (7) GIT Environment Setup (8) GIT Terminology (9) GIT Command (10) Git Config Command (11) Git Init Command (12) Git Clone Command (13) GIT Checkout Command (14) Git Add Command (15) Git Commit Command (16) Git Status Command (17) Git Push Command (18) Git Pull Command (19) Git Branch Command (20) Git Merge Command (21) GIT Merge Conflict (22) Git Log Command (23) Git
-

How To Plot Numpy Arrays?
How To Plot Numpy Arrays? Table Of Contents: Using ‘matplotlib’ Library To Plot The Numpy. Examples Of Plotting. Example-1 import matplotlib.pyplot as plt %matplotlib inline a = np.array([2, 1, 5, 7, 4, 6, 8, 14, 10, 9, 18, 20, 22]) plt.plot(a) Example-2 import matplotlib.pyplot as plt %matplotlib inline x = np.linspace(0, 5, 20) y = np.linspace(0, 10, 20) plt.plot(x, y, ‘purple’) # line plt.plot(x, y, ‘o’) # dots Example-3 import matplotlib.pyplot as plt %matplotlib inline fig = plt.figure() ax = fig.add_subplot(projection=’3d’) X = np.arange(-5, 5, 0.15) Y = np.arange(-5, 5, 0.15) X, Y = np.meshgrid(X, Y) R = np.sqrt(X**2 +
-

How To Save And Load NumPy Objects?
How To Save And Load NumPy Objects? Table Of Contents: np.save np.savez np.savetxt np.load np.loadtxt (1) np.save(): Save an array to a binary file in NumPy .npy format. Syntax: numpy.save(file, arr, allow_pickle=True, fix_imports=True) Parameters: file: file, str, or pathlib.Path – File or filename to which the data is saved. If the file is a file object, then the filename is unchanged. If the file is a string or Path, a .npy the extension will be appended to the filename if it does not already have one. arr: array_like – Array data to be saved. allow_pickle: bool, optional – Allow saving object arrays
-

How To Access The Docstring For More Information?
How To Access The Docstring For More Information? Table Of Contents: help( ) ? ?? (1) help () ‘help( )’ method is used to get information about an object. It will provide you with a quick and concise summary of the object and how to use it Syntax: help([object]) Note: You need to pass the object name to get the information about it. Example-1: help(np.ravel) Help on function ravel in module numpy: ravel(a, order=’C’) Return a contiguous flattened array. A 1-D array, containing the elements of the input, is returned. A copy is made only if needed. As of NumPy
