-
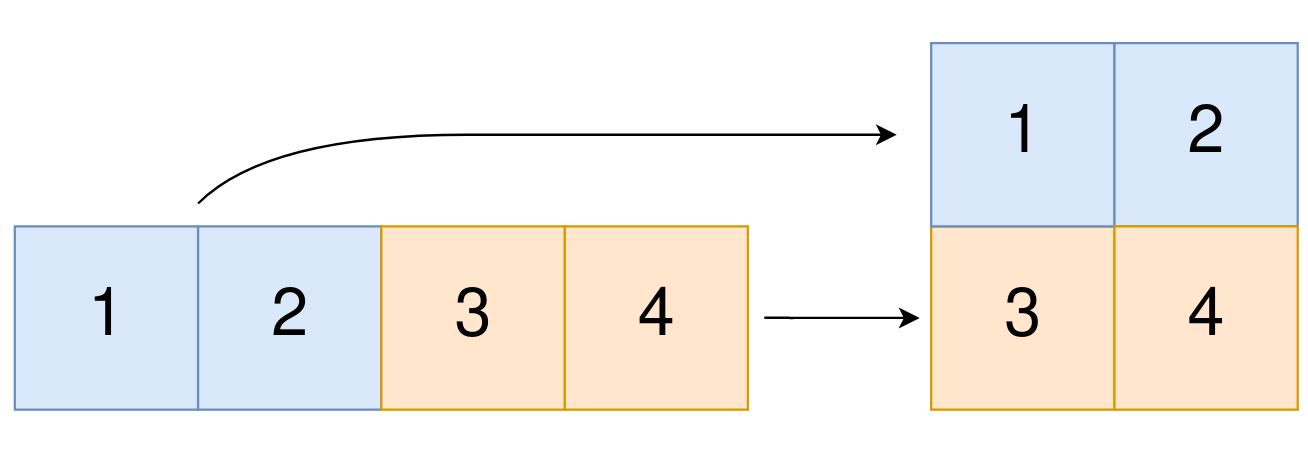
How To Convert A 1D Array Into A 2D Array?
How To Convert A 1D Array Into A 2D Array? Table Of Contents: np.newaxis np.expand_dims (1) np.newaxis Using np.newaxis will increase the dimensions of your array by one dimension when used once. This means that a 1D array will become a 2D array, a 2D array will become a 3D array, and so on. You can explicitly convert a 1D array with either a row vector or a column vector using np.newaxis. For example, you can convert a 1D array to a row vector by inserting an axis along the first dimension. Example-1: a = np.array([1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6]) a array([1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6]) a.shape (6,) Adding
-

How To Reshape A Numpy Array ?
How To Reshape A Numpy Array ? Table Of Contents: numpy.reshape( ) Examples Of numpy.reshape( ) (1) numpy.reshape( ) Syntax: numpy.reshape(a, newshape, order=’C’) Parameters: a: array_like – Array to be reshaped. newshape: int or tuple of ints – The new shape should be compatible with the original shape. If an integer, then the result will be a 1-D array of that length. One shape dimension can be -1. In this case, the value is inferred from the length of the array and the remaining dimensions. order: {‘C’, ‘F’, ‘A’}, optional – Read the elements of a using this index order, and place
-

How Do You Know The Shape and Size Of a Numpy Array ?
How Do You Know The Shape and Size Of a Numpy Array ? Table Of Contents: ndarray.ndim ndarray.size ndarray.shape (1) ndarray.ndim ndarray.ndim will tell you the number of axes, or dimensions, of the array. Example-1: a = np.array([1, 2, 3]) a array([1, 2, 3]) a.ndim Output: 1 Example-2: b = np.array([[1,4],[3,2]]) b array([[1, 4], [3, 2]]) b.ndim Output: 2 Example-3: c = np.array([[[1,4],[3,2]]]) c array([[[1, 4], [3, 2]]]) c.ndim Output: 3 Example-4: y = np.zeros((2, 3, 4)) y array([[[0., 0., 0., 0.], [0., 0., 0., 0.], [0., 0., 0., 0.]], [[0., 0., 0., 0.], [0., 0., 0., 0.], [0., 0., 0.,
-

How To Remove Elements From Numpy Array?
How To Remove Elements From Numpy Array? Table Of Contents: np.delete( ) Examples Of np.delete() Method. (1) np.delete( ) A copy of arr with the elements specified by obj removed. Note that delete does not occur in-place. If axis is None, out is a flattened array. Syntax: numpy.delete(arr, obj, axis=None) Parameters: arr: array_like – Input array. obj: slice, int or array of ints – Indicate indices of sub-arrays to remove along the specified axis. axis: int, optional – The axis along which to delete the subarray defined by obj. If axis is None, obj is applied to the flattened array. Returns: out: ndarray – A copy of arr with the elements specified by obj removed. Note that delete does not occur
-

How To Sort A Numpy Array ?
How To Sort A Numpy Array? Table Of Contents: np.sort( ) Examples Of Sorting Numpy Array. (1) np.sort( ) Return a sorted copy of an array. Syntax: numpy.sort(a, axis=-1, kind=None, order=None) Parameters: a: array_like – Array to be sorted. axis: int or None, optional – Axis along which to sort. If None, the array is flattened before sorting. The default is -1, which sorts along the last axis. kind: {‘quicksort’, ‘mergesort’, ‘heapsort’, ‘stable’}, optional – Sorting algorithm. The default is ‘quicksort’. order: str or list of str, optional – When a is an array with fields defined, this argument specifies which fields to
-

How To Add Numpy Arrays ?
How To Add Numpy Arrays ? Table Of Contents: ‘+’ Operator np.concatenate() (1) ‘+’ Operator The ‘+’ operator will ‘sum’ the elements of numpy array. Example-1 a = np.array([1,2,3,4,5]) b = np.array([6,7,8,9,10]) a + b Output: array([ 7, 9, 11, 13, 15]) Example-2 a = np.array([1,2,3,4,5]) b = np.array([6,7,8,9,10]) c = np.array([11,12,13,14,15]) a + b + c Output: array([18, 21, 24, 27, 30]) (2) np.concatenate() Join a sequence of arrays along an existing axis. Syntax: numpy.concatenate((a1, a2, …), axis=0, out=None, dtype=None, casting="same_kind") Parameters: a1, a2, …sequence of array_like – The arrays must have the same shape, except in the dimension
-
How To Create Numpy Array ?
How To Create Numpy Array ? Table Of Contents: np.array( ) np.zeros( ) np.ones( ) np.empty( ) np.arange( ) np.linspace( ) (1) np.array( ) To create a NumPy array, you can use the function np.array(). All you need to do to create a simple array is, pass a list to it. you can also specify the type of data in your list. Example-1 import numpy as np lst = [1,2,3,4,5,6] a = np.array(lst) a Output: array([1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6]) (2) np.zeros( ) You can also create an array which will contain only zeros. np.zeros( ) will take an integer
-

How To Import Numpy?
How To Import Numpy? Table Of Contents: Importing Numpy Module. Example Of Using NumPy Module. (1) Importing Numpy Module. Syntax: import numpy as np (2) Example Of Using Numpy Module. a = np.arange(6) a Output: array([0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5]) Note: An array of ‘6’ elements.
-

How To Install NumPy?
How To Install NumPy? Table Of Contents: Install Using ‘pip’. Install Using ‘conda’ (1) Install Using ‘pip’ : Recommended Syntax: pip install numpy (2) Install Using ‘conda’ Syntax: conda install numpy
-

Welcome To Numpy !!
Welcome To Numpy !! Table Of Contents: What Is NumPy? Why Use NumPy? Applications Of Numpy? (1) What Is Numpy ? ‘Numpy’ is a ‘Python’ package which is designed for performing heavy mathematical computation. If your work field is related to Science and Math then it’s your go-to library. ‘Numpy’ is based on a ‘ndarray’, This encapsulates n-dimensional arrays of homogeneous data types. (2) Why Use Numpy ? NumPy arrays are faster and more compact than Python lists. An array consumes less memory and is convenient to use. NumPy uses much less memory to store data and it provides a mechanism
