-
Introduction To NLP!
Introduction To NLP Table Of Contents: What Is Natural Language? Features OF Natural Language. Natural Language Vs. Programming Language. What Is Natural Language Processing? Fundamental Task NLP Perform: Common NLP Tasks: Techniques and Approaches: Applications Of NLP. Models Used In NLP. Specific Models In NLP. (1) What Is Natural Language? Natural Language refers to the language that humans use to communicate with each other, including spoken and written forms. It encompasses the complex and nuanced ways in which humans express themselves, including grammar, syntax, semantics, pragmatics, and phonology. Natural Language is characterized by its variability, ambiguity, and context dependency, making
-

Gated Recurrent Unit (GRUs).
Gated Recurrent Units(GRUs) Table Of Contents: Disadvantages Of LSTM Networks. What Is GRU? Why We Need GRU Neural Network? (1) Disadvantages Of LSTM Networks. Computational Complexity: LSTM networks are more computationally complex compared to simpler architectures like feedforward neural networks or basic RNNs. This complexity arises due to the presence of multiple gates, memory cells, and additional parameters. As a result, training and inference can be more computationally expensive and time-consuming, especially for large-scale models and datasets. Memory Requirement: LSTM networks require more memory to store the additional parameters and memory cells. This can pose challenges when working with limited
-
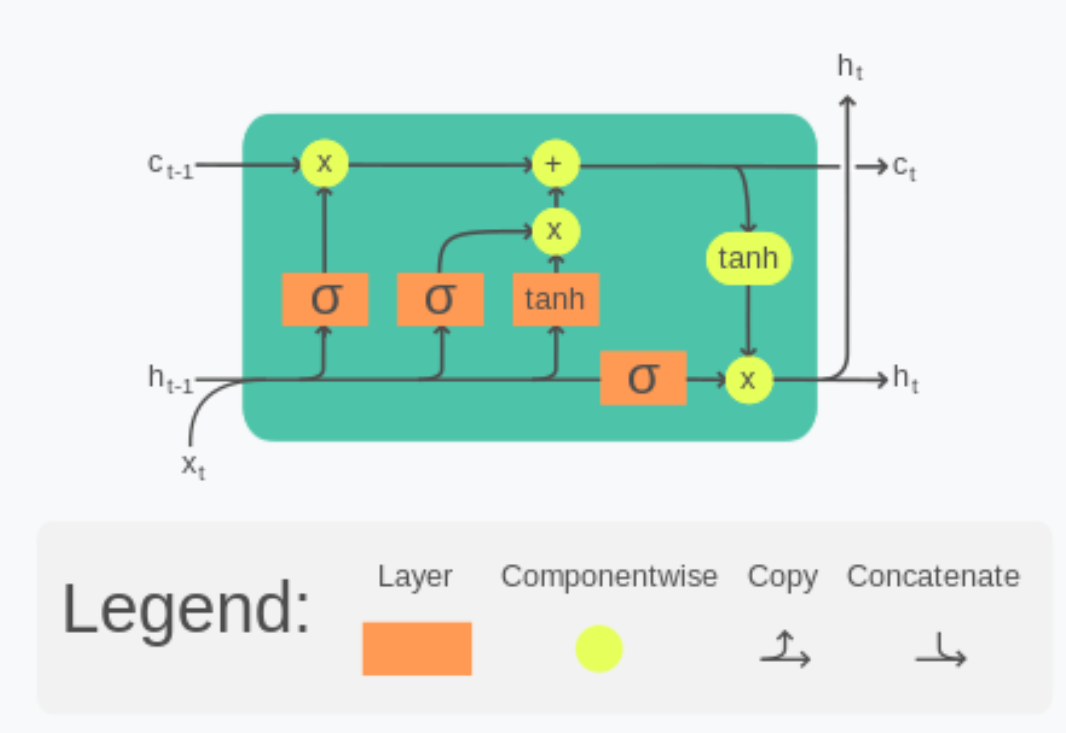
Maths Behind LSTM Networks.
Architecture Of LSTM Networks Table Of Contents: Architectural Diagram Of LSTM Network. (1) Architectural Diagram Of LSTM Network. (2) Inputs For LSTM Network. An LSTM network takes three inputs as its parameter. Previous Time Stamp Cell State Value. Previous Time Stamp Hidden State Value. Current Time Stamp Input State. (2) Outputs For LSTM Network. An LSTM network has two outputs. Current Cell State Value. Current Hidden State Value. (3) Core Idea Of LSTM Network. An LSTM unit is like a box whose main purpose is to store some important words and give them as an output. Which words to store
-
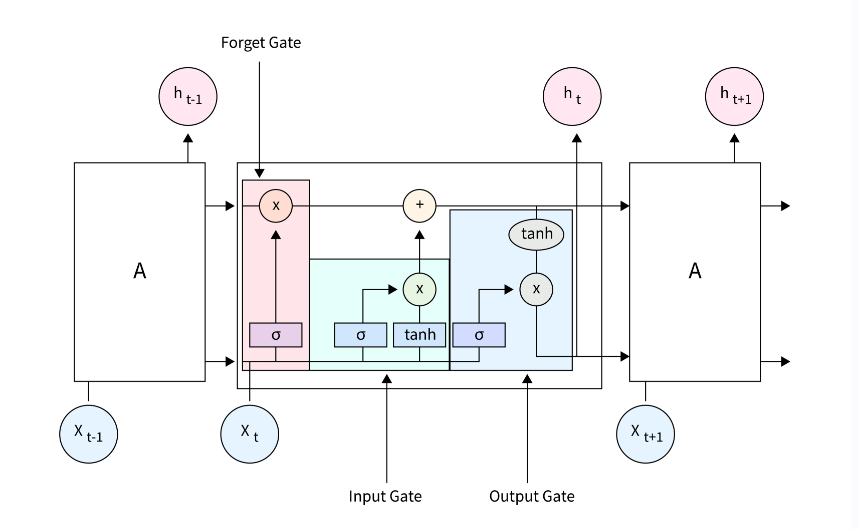
Long Short Term Memory Network.
Long Short Term Memory Network Table Of Contents: Problem With ANN. Problem With RNN Core Ideas Behind LSTM Working Principle Of LSTM Difference Between RNN & LSTM Architecture Of LSTM Network. (1) Problem With ANN Problem-1: Sequence Is Lost The problem with ANN architecture is that its design is unable to process sequential information. When we pass sequential information to the ANN network we have to pass everything at a time. When we pass every word at a time It’s sequence will be lost in the process. We will not be able to know which word comes after what. Problem-2:
-

Vanishing & Exploding Gradient Problem In RNN.
Vanishing & Exploding Gradient Table Of Contents: Vanishing & Exploding Gradient. What Is Vanishing Gradient? What Is Exploding Gradient? Solution To Vanishing & Exploding Gradient. (1) Vanishing & Exploding Gradient The vanishing and exploding gradient problems are common challenges in training recurrent neural networks (RNNs). These problems occur when the gradients used to update the network’s parameters during training become either too small (vanishing gradients) or too large (exploding gradients). This can hinder the convergence of the training process and affect the performance of the RNN model. (2) Vanishing Gradient During backpropagation, the calculation of (partial) derivatives/gradients in the weight update formula follows
-

Recurrent Neural Network.
Recurrent Neural Network Table Of Contents: What Are Recurrent Neural Networks? The Architecture of a Traditional RNN. Types Of Recurrent Neural Networks. How Does Recurrent Neural Networks Work? Common Activation Functions. Advantages And Disadvantages of RNN. Recurrent Neural Network Vs Feedforward Neural Network. Backpropagation Through Time (BPTT). Two Issues Of Standard RNNs. RNN Applications. Sequence Generation. Sequence Classification. (1) What Is Recurrent Neural Network? Recurrent Neural Network(RNN) is a type of Neural Network where the output from the previous step is fed as input to the current step. In traditional neural networks, all the inputs and outputs are independent of each other.
-

Why ANN Can’t Be Used In Sequential Data?
Why ANN Can’t Be Used In Sequential Data? Table Of Contents: Input Text Having Varying Size. Zero Padding – Unnecessary Computation. Prediction Problem On Different Input Length. Not Considering Sequential Information. Reason-1:Input Text Having Varying Size. In real life, input sentences will have different word counts. Suppose you make an ANN having the below structure. It has 3 input nodes. Our first sentence contains 6 words, hence the weight metrics will be 6 * 3 structure. The second sentence contains 3 words hence the weight metrics will be 3 * 3 structure. The third sentence contains 4 words hence the weight
-
Sequential Data
Gradient Descent Optimizer Table Of Contents: What Is Sequential Data? Key Characteristics Of Sequential Data. Examples Of Sequential Data. Why Is Sequential Data Is An Issue For The Traditional Neural Network? (1) What Is Sequential Data? Sequential data is data arranged in sequences where order matters. Data points are dependent on other data points in this sequence. Examples of sequential data include customer grocery purchases, patient medical records, or simply a sequence of numbers with a pattern. In sequence data, each element in the sequence is related to the ones that come before and after it, and the way these
-
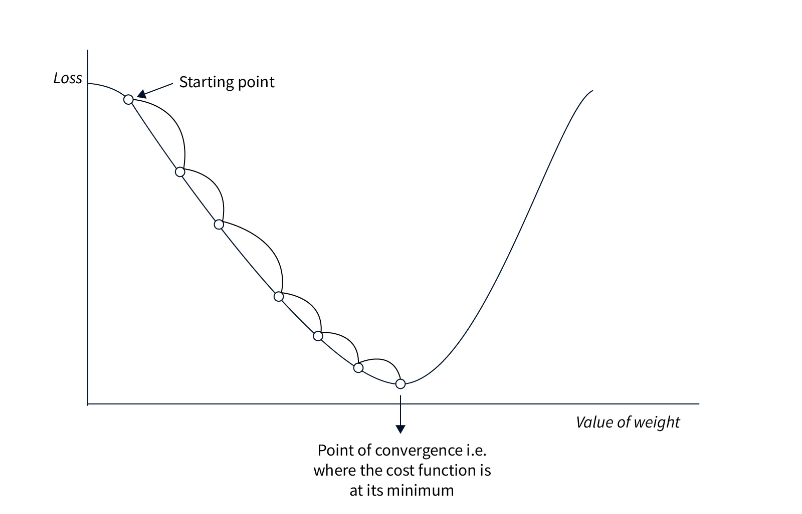
Gradient Descent Optimizer
Gradient Descent Optimizer Table Of Contents: What Is Gradient Descent Algorithm? Basic Gradient Descent Algorithms. Batch Gradient Descent. Stochastic Gradient Descent (SGD). Mini-Batch Gradient Descent. Learning Rate. What Is The Learning Rate? Learning Rate Scheduling. Variants of Gradient Descent. Momentum. Nesterov Accelerated Gradient (NAG). Adagrad. RMSprop. Adam. Optimization Challenges Local Optima Plateaus and Vanishing Gradients. Overfitting. (1) What Is Gradient Descent Algorithm? The Gradient Descent algorithm is an iterative optimization algorithm used to minimize a given function, typically a loss function, by adjusting the parameters of a model. It is widely used in machine learning and deep learning to update
-

Cost Functions In Deep Learning.
Cost Functions Table Of Contents: What Is A Cost Function? Mean Squared Error (MSE) Loss. Binary Cross-Entropy Loss. Categorical Cross-Entropy Loss. Custom Loss Functions. Loss Functions for Specific Tasks. Loss Functions for Imbalanced Data. Loss Function Selection. (1) What Is A Cost Function? A cost function, also known as a loss function or objective function, is a mathematical function used to measure the discrepancy between the predicted output of a machine learning model and the actual or target output. The purpose of a cost function is to quantify how well the model is performing and to guide the optimization process
